Buy official publications by phone: * We will be happy to make a selection of standards for your activities. Call! (499) 110-91-64 - Your personal manager in Moscow and in all cities of Russia (Moscow, Kasatkina str., 11) (812) 407-22-64 - Your personal manager in St. Petersburg (St. Petersburg , Sinopskaya embankment, 22) * The website contains an abbreviated list of standards.
Attention! From us you can buy other Sanitary Regulations and mandatory logs (filling out), as well as ready-made sets of kits for your type of activity: medical, pharmaceutical, catering, beauty salons, manufacturing, retail and wholesale trade, temporary residence, sports, educational and any other activity. All publications are official.
SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for organizations engaged in medical activities”
SanPiN 2.1.2.2631-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the location, structure, equipment, maintenance and operating hours of public utility organizations providing hairdressing and cosmetic services”
SP 3.1/3.2.1379-03 “General requirements for the prevention of infectious and parasitic diseases”
SanPin 2.1.2.2645-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for living conditions in residential buildings and premises”
SanPiN 2.1.2.2646-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the design, maintenance and operating hours of laundries”
SP 1.1.1058-01 “Organization and conduct of production control over compliance with sanitary rules and implementation of sanitary and anti-epidemiological (preventive) measures”
SP 1.1.2193-07
SanPiN 2.17.728-99 “Rules for the collection, storage and disposal of healthcare facility waste”
SanPin 2.1.41074-01 “Drinking water. Hygienic requirements for water quality of centralized drinking water supply systems. Quality control"
SN 2.2.4/2.1.8.562-96 “Noise in workplaces, in residential and public buildings and in residential areas”
SanPiN 2.2.2/2.413402-03 “Hygienic requirements for personal electronic computers and work organization”
SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1278-03 “Hygienic requirements for natural, artificial and combined lighting of residential and public buildings”
SanPiN 2.0555-96 “Hygienic requirements for working conditions for women”
SanPiN 2.2.4.548-96 “Hygienic requirements for the microclimate of industrial premises”
SP 3.1.1.2521-09 “Prevention of cholera. General requirements for epidemiological surveillance of cholera in the Russian Federation
SP 3.5.1378-03 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the organization and implementation of disinfection activities”
SP 3.5.3.1129-02 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for deratization”
MU 3.5.736-99 “Technology for processing linen in medical institutions”
SanPiN 2.4.4.3155-13 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the design, maintenance and organization of work of inpatient recreation and health organizations for children”
SanPiN 2.1.7.2790-10 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the management of medical waste”
SanPiN 2.3.4.050-96. 2.3.4. Enterprises of the food and processing industry (technological processes, raw materials). Production and sale of fish products
Unified sanitary-epidemiological and hygienic requirements for goods subject to sanitary-epidemiological supervision (control)
Other positions. Please check availability by phone in Moscow and St. Petersburg.
The company’s activities in Russia are invariably linked to sanitary and epidemiological norms and rules. They regulate almost all processes of the organization, taking care of the safety of citizens and nature. If you ignore these requirements, you can easily end up on the list of companies (LLC, individual entrepreneurs) that violate Federal Law No. 52-FZ “On the sanitary and epidemiological welfare of the population,” which indicates the need to have officially published sanitary rules, methods and techniques for controlling factors habitats.
Requirements
Standardized labeling indicators are specified in the regulatory document GOST 22046-2016 “Furniture for educational institutions. General technical conditions". This standard was approved by the Interstate Council for Standardization and is applied throughout Russia. According to this legislative draft, the bulk purchase of student equipment is permitted, which has undergone a preliminary strength test, taking into account the relevant documentation.
What is taken into account when drawing up a school schedule: basic criteria.
As a rule, the head teacher is responsible for drawing up the schedule. This task must reflect all the requirements of regulatory documents that serve as a fulcrum in the distribution of items.
What to consider when creating a schedule:
- Required number of hours in each subject for each class.
- Uniform distribution of hours among teachers.
- Biorhythms of students.
- Age of students and permissible maximum daily workload.
- Additional classes.
In addition to the need to distribute lessons between classes in a sufficient number of hours to master the material, it is important to take into account the biorhythms of students.
Everyone remembers from school that the most difficult subjects and tests always fell in the middle of the week. There are other patterns as well.
Difficult subjects in the schedule.
Requirements for complex subjects in the school schedule:
- The most activity by day of the week occurs on Tuesday and Wednesday. On Thursday, students already begin to get tired; on this day the workload decreases. On Monday, the children had not yet “swinged up” after the day off. Saturday has always been the shortest and easiest day.
- Activity during the day also occurs in the second and third lessons. This time is approximately from 10 to 12 noon. It is best for teachers to assign tests during these hours. And when drawing up a schedule, the most difficult subjects are assigned to these hours.
- Physical education is most often placed closer to the last lessons. After physical education, it is not recommended to carry out complex tests, since the children’s attention will be unfocused.
- Lessons that do not require serious mental stress are scheduled on Monday, Friday or Saturday. These are works, music.
Additional workload is also taken into account: work of clubs, extracurricular activities in subjects, preparation for exams.
Most of these requirements are regulated by SanPiN.
Business Solutions
- shops clothing, shoes, groceries, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
Furnished products for student use must have the following parameters:
- The gloss of the coating is no more than 49%.
- The working surface is easy to clean from dirt. Science classroom tables are equipped with a protective layer against chemicals.
- Compliance with all epidemiological standards.
The dimensions of educational furniture and its marking at school (according to SanPiN) are far from the only conditions that must be met. Requirements are also put forward for assembly:
- Reliable fixation of all structural parts.
- Impossibility of manually separating hardware elements.
- The absence of any irregularities on the outer surface. Sharp edges are rounded and holes in metal pipes with a diameter greater than 7 mm are closed or hidden.
- Contaminating parts are hidden.
GOST 22360-95 regulates the proper fixation of large objects:
- A strong and immovable connection of all parts of the structure and the impossibility of disassembling it manually.
- Reliable fastening of the stand (if available) to the object.
Furniture used in educational institutions must have special markings, which are indicated in Russian or the official regional language. It is prohibited to make any marks on the work surface. Tables are marked using special colored stickers that correspond to the height categories of GOST 11015 and 11016.
Desk number (according to Sanitary Regulations) and the size of educational furniture according to the student’s height, table
Experts have developed a size table that provides for the division of furniture into 6 groups. Such a classification makes it possible to differentiate it depending on the growth of children, thanks to which they can sit safely and comfortably at tables without damaging their eyesight or posture while doing any work (reading, writing, drawing and much more).
How many height sizes are there for school furniture?
The size chart is based on various indicators: the height of the child, the height of the table and chair. Then the distribution and selection of optimal furniture products were carried out, which are manufactured for use in educational institutions. Today there are 6 main groups. There is also a zero one, but it is relevant for preschool institutions. The first two groups are practically not used, since they assume the height of first-graders to be less than 130 cm.
The above table for the size of desks in elementary schools according to SanPiN will help to compare the requirements of the standards with actual readings. With its help, you can correctly (from the legal point of view) purchase and arrange equipment that will pass any inspections and also ensure the most comfortable learning process.
Rules for everyone
SanPiN is assigned a number that identifies it among others. Knowledge of the norms and rules that are presented in the documents will allow you to avoid numerous mistakes and difficulties when working with clients.
In order not to be punished, purchase Sanitary Regulations, as well as journals that are required to be maintained in your company.
Contact our company and you will receive all the necessary information. With us, your activities will be legal.
Publishing activities and printing of your creativity by our own forces with our own distribution base! Call!
Equipment of premises according to GOST
Each individual auditorium or class in educational institutions must be equipped taking into account the standard established by law. The arrangement of offices varies depending on its purpose. However, an important point is the need for all interior items.
Classrooms

Taking into account GOST 22046-2016, the audience includes:
- Desks.
- Chairs.
- Teacher's desk.
- Benefit lockers.
Additionally, there may be a wardrobe, a bedside table for storing posters and shelves for various purposes.
Library
The main task of the library is to provide children with access to the literary archive, as well as works that are included in the school curriculum. These can be magazines, popular science publications, textbooks, etc. In addition, all books issued for the period of study are stored here. Necessary:
- wide cabinets for textbooks and manuals;
- chairs;
- reading tables.
Also, marking school furniture according to SanPiN may be necessary for sofas, shelves and stands.
Dining room
This is a wide and spacious room that can accommodate many children during lunch breaks. It will require both perfect compliance with sanitary standards and a beautiful interior. Mandatory components of the dining room are:
- Dining tables of different sizes (large, medium and small).
- Benches or chairs.
Assembly Hall
It is used for festive celebrations and various events. Its main task is the ability to accommodate many spectators who can fully observe what is happening on stage. In parallel with this, it is necessary to ensure easy change of furniture for the assembly hall and the possibility of its removal to other rooms for holding public meetings. Based on this requirement, the mandatory elements of the halls are connected and separate chairs.
No additional furniture items are needed here. This is due to the fact that the main emphasis is on stage organization and technical equipment for performance and sound reinforcement.

Subject classrooms
They involve conducting various experiments and laboratory work using various devices and chemicals. For the physics classroom you need:
- stands;
- laboratory tables;
- teaching table for demonstration;
- cabinets for reagents with symbols.
There are no particularly stringent requirements for classrooms where subjects such as fine arts and drawing are taught. Classes are held on standard desks, but wooden easels and drawing boards are useful for comfortable studying.
At the personal request of the management (director), it is possible to additionally place separate wardrobe lockers for students, which replace the classic hooks in the corridor.
Requirements GOST 30494-2011:
There are no special requirements for school buildings in this GOST 30494, but there are general requirements for public and administrative buildings.
According to clause 4.4 and table 3 of GOST 30494-2011, the optimal and permissible standard air temperature in the service area of public and administrative buildings should be within the limits:
During the cold season:
- rooms of the 1st category (rooms in which people in a lying or sitting position are in a state of rest and rest): optimal 20-22°C, acceptable 18-24°C;
- rooms of the 2nd category (rooms in which people are engaged in mental work, study): optimal 19-21°C, acceptable 18-23°C;
- premises of category 3a (rooms with large numbers of people, in which people are mainly in a sitting position without street clothes): optimal 20-21°C, acceptable 19-23°C;
- premises of category 3b (rooms with large numbers of people, in which people are mainly in a sitting position in street clothes): optimal 14-16°C, acceptable 12-17°C;
- rooms 3 in category (rooms with large numbers of people, in which people are mainly in a standing position without street clothes): optimal 18-20°C, acceptable 16-22°C;
- rooms of the 4th category (rooms for outdoor sports): optimal 17-19°C, acceptable 15-21°C;
- rooms of the 5th category (rooms in which people are scantily clad (locker rooms, treatment rooms, doctors' offices, etc.)): optimal 20-22°C, acceptable 20-24°C;
- premises of the 6th category (premises with temporary occupancy of people (lobbies, dressing rooms, corridors, stairs, bathrooms, smoking rooms, storage rooms)): optimal 16-18°C, acceptable 14-20°C;
- Bathrooms, showers: optimal 24-26°C, acceptable 18-28°C;
During the warm season:
- Premises with constant presence of people (a room in which people stay for at least 2 hours continuously or 6 hours in total during the day): optimal 23-25°C, acceptable 18-28°C.
According to clause 4.6, when ensuring microclimate indicators at various points in the service area, an air temperature difference of no more than 2°C is allowed for optimal indicators and 3°C for acceptable ones.
In accordance with clause 4.7, in public buildings in accordance with regulatory and technical documents (SP 60.13330.2016 Heating, ventilation and air conditioning. Updated edition of SNiP 41-01-2003) during the cold period of the year during non-working hours, it is allowed to reduce microclimate indicators by taking the air temperature below the normalized value, but not below:
- 12°C - in public, administrative and domestic premises.
The normalized temperature must be ensured before use.
Relative air humidity in schools according to GOST and SanPiN standards
Business Solutions
- the shops
clothes, shoes, products, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
Standard dimensions of furniture and its markings
State standards clearly describe the amount of space required for all types of products, as well as their required height. Eg:
- GOST 18314-93. Tables for laboratory work: dimensions according to height markings; 2-seater with a working area of 1300 mm and 3-seater with 1950 mm are possible; the height of the boot along the lid is less than 60 mm.
- GOST 19549-93. Furnished products for drawing: dimensions according to height markings; corners of the stand and desk lids with rounded edges within a radius of at least 10 - 30 mm; the location of removable music stands is at least 300-400 mm from the lid.
- GOST 5994-93. The width of the hinged lid (if available) is from 10 to 180 mm; 2-seaters are equipped with space of 450x270 centimeters for briefcases; the surface of the seats is flat or with a recess in the center of no more than 10 mm; corners of the table and desk top with rounded corners within a radius of at least 10-30 mm.
Why do you need labeling of cleaning equipment?
Labeling cleaning equipment according to SanPiN, a sample of which is given in this article, is necessary to prevent cross-contamination of pathogens during cleaning of different areas of the same institution. The marking of equipment for cleaning premises is regulated by a set of Sanitary Rules and Standards.
From January 1, 2021, the Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Inspector of the Russian Federation dated May 18, 2010 No. 58 (as amended on June 10, 2016) “On approval of SanPiN 2.1.3.2630-10” became invalid.
And a new decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated December 24, 2020 No. 44 “On approval of sanitary rules SP 2.1.3678-20 “Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the operation of premises, buildings, structures, equipment and transport, as well as the conditions of business activities” came into force entities engaged in the sale of goods, performance of work or provision of services" (Registered with the Ministry of Justice of Russia on December 30, 2020 No. 61953).
Materials

For products installed in educational institutions, soft wood and plastic are used in production. Based on GOST 30255-95, the use of raw materials even with a minimal content of toxic substances is prohibited. Desks and bookcases are made from chipboard with class E1, chairs are made from solid wood or solid wood. The internal part is sealed with PVC sheets. Metal frames are treated with polymer paint. It is also used to cover tables for chemistry and physics classes, as it increases resistance to chemicals. Marking furniture in schools according to SanPiN requires mandatory treatment of wooden products with a special varnish.
The material can be considered suitable if the following conditions are met:
- No foreign fluff, unevenness or roughness.
- There are no unpleasant or pungent odors.
- There is no contamination with radionuclides (the maximum permitted background is less than 300 Bq per 1 kg of weight).
- Resistant to heat and chemicals.
- Low thermal conductivity (less than 0.46 W).
Requirements SP 2.4.3648-20 (valid from 01/01/2021):
clause 2.7. Microclimate, heating and ventilation in facilities must meet the following requirements:
clause 2.7.1. Buildings are equipped with heating and ventilation systems in accordance with the requirements for heating, ventilation and air conditioning in public buildings and structures in accordance with the legislation on technical regulation in the field of safety of buildings and structures.
The premises are provided with microclimate and air exchange parameters determined by the requirements of hygienic standards.
The maximum permissible concentrations of pollutants determined by the requirements of hygienic standards are not allowed to be exceeded in the air.
The use of portable heating devices with infrared radiation is not permitted.
clause 2.7.2. The design of windows should ensure the possibility of ventilation of premises at any time of the year (with the exception of children's playrooms located in shopping, entertainment and cultural leisure centers, pavilions, airports, railway stations and other non-residential facilities).
Ventilation is not carried out in the presence of children.
clause 2.7.3. Air temperature control in all rooms intended for children and youth is carried out by the Organization using thermometers.
clause 2.7.4. Premises where equipment is installed that is a source of dust, chemicals, excess heat and moisture are additionally provided with a local exhaust ventilation system.
Each group of premises (industrial, warehouse, sanitary) is equipped with separate supply and exhaust ventilation systems with mechanical and (or) natural impulse.
An inspection of the technical condition of the ventilation system (inspection, cleaning and efficiency monitoring) is carried out before putting the building into operation, then 2 years after commissioning, and subsequently at least once every 10 years. When examining the technical condition of ventilation, instrumental measurements of air exhaust volumes should be carried out.
clause 2.7.5. Enclosing devices of heating devices must be made of materials that are harmless to the health of children.
Fences made of particle boards are not allowed.
Color and design
The correct selection of shade when creating furniture for student use plays an important role and is partly controlled by GOST 22046-2016. There is a color marking for furniture group 5 (desks) in a school according to SanPiN. The standard provides restrictions:
- Darkened details are allowed in the design of various stands for school supplies, as well as bookcases with light elements.
- The use of white desks is prohibited (excluding metal fastenings).
- According to Appendix A, it is recommended to give preference to a cold pastel palette for upholstery or paintwork.
SanPin standards for schools.
If the above rules are the basis on which to rely when drawing up a schedule, then the requirements of SanPin must be followed exactly.
If they are violated, the school may pay a fine. If necessary, the test can be scheduled on Saturday or Monday, and physical education can be done at the beginning of the day.
The whole school cannot play sports in one gym at the same time. There are other reasons for deviating from the rules.
For example, when students fall ill with acute respiratory infections and flu in large numbers, classes are cancelled. And after quarantine we have to make up for lost time.
Classes can be conducted more intensively; both the first and last days of the week are loaded in order to have time to cover the material.
Also, the absence of teachers periodically forces the schedule to change, deviating from the intended rules.
SanPiN norms cannot be violated, whatever the reasons. According to SanPiN, the school bell schedule cannot change significantly.
Hours may be reduced due to a reduction in teaching time under certain circumstances, but an increase is unacceptable.
Sanpin for schools: as amended 2021.
How desks are marked in elementary school
Markings are applied to the visible side of chairs and desks in the form of classic circles with a diameter of 1-3 centimeters or colored stripes. The most convenient places for tables are: side leg, back surface, edge, if the lid is wide enough. Markings on chairs are carried out in the area of the rear surface of the back, the visible upper part of the metal frame.
The marking standards recommend that this be done symmetrically on both sides of any furniture used in educational institutions. Thanks to this, schoolchildren will quickly get used to the rules and will be able to navigate if necessary to change it to the desired size.
Where to get the material
Not all manufacturers are worried about the fact that after furniture products leave the assembly line for the warehouse and facility, desks and tables in an elementary school should be marked according to Sanitary Regulations and Regulations. High-quality pre-sale preparation is observed only with expensive samples. But unfortunately, not everyone has the limits of specifications and the ability to replace them with alternative options. Marking is only part of the options included in the main kit.
If it is impossible to receive the furniture in a prepared form, Cleverence will be able to solve this problem. We have at our disposal a marking kit with an excellent adhesive base, which is highly resistant to solar fading and abrasion that occurs during active and long-term use. If for some reason re-gluing is required, this base easily reverses lumps and is removed without the slightest residue.
How to mark the numbers of desks and chairs by height (SanPiN)
Student furniture products must be marked taking into account the height group of the children who will study behind them. There is a single classification that remains unchanged and mandatory for all educational institutions. It includes several indicators: height group, marked color, table and chair height. On this basis, the following are distinguished:
- First: 110 - 115 cm, orange, 46 and 26 cm.
- Second: 115 - 130 cm, purple, 52 and 30 cm.
- Third: 130 - 245 cm, yellow, 58 and 34 cm.
- Fourth: 145 - 160 cm, red, 64 and 38 cm.
- Fifth: 160 - 175 cm, green, 70 and 42 cm.
- Sixth: over 175 cm, blue, 76 and 46 cm.
There is also a zero group that is not included in the main table. As a rule, it is installed in kindergartens and other preschool institutions. It is applicable for children whose height does not exceed 95 centimeters. The first and second categories are not common, since the average height of a child entering first grade is approximately 130 cm.
Cleaning equipment for medical institutions
Carts, mops, containers, rags, mops must be clearly marked or color-coded taking into account the functional purpose of the premises and types of cleaning work and must be stored in a designated area. The rags are marked as follows: rags for cleaning in staff rooms and wards are marked in blue; red - for cleaning bathrooms; green – dressing rooms, treatment rooms; yellow – utility rooms.
A color coding scheme for cleaning equipment in medical institutions should be located in the equipment storage area.
Toilet cleaning equipment must be color coded to indicate special attention. Cleaning equipment for the toilet: rags, buckets, brushes are labeled and stored separately from other cleaning equipment.
Equipment for cleaning toilets must be clearly marked in red, which is used in areas with a high degree of bacterial contamination. In the specialized literature there is often a definition that cleaning equipment for cleaning bathrooms must have a signal marking .
Should cleaning equipment for production, utility and auxiliary premises be marked with paint ? – the answer to this question is definitely “Yes!” Also, such cleaning equipment should be stored in separate rooms equipped with special washing baths ( washing equipment ) and drainage devices with hot and cold water supply, as well as a register for drying cleaning equipment.
Equipment

The marking of furniture and its dimensions at school are determined by special labels. Use allows you to easily remove them from the surface without leaving adhesive residues. They do not interfere with students, are not conspicuous and can withstand any temperature changes.
Regardless of the selected technical equipment, the labeling content must necessarily include:
- Manufacturer information.
- His contact details.
- Trademark.
- Date of manufacture, warranty period.
- Description of the purpose of the item.
- A note about the current standard.
Adhering to these requirements of SanPiN, marking of desks and chairs (height) will be carried out correctly, from a legal and safe point of view.
Today, the issue of arranging classrooms in educational institutions is approached as strictly, responsibly and under the careful control of the rules established by law. These quality standards, which become even more convenient every year, are aimed at taking care of students of all ages. Compliance with all established standards greatly simplifies the life of both the student and the management. Knowing the requirements put forward by GOST will allow you to choose the right furniture manufacturer who will provide the required desk number according to height.
The learning process should always take place in a favorable atmosphere and cozy environment.
The creation of such conditions falls entirely on the shoulders of the director and the working team (educators, teachers and lecturers), who are responsible for the life and health of students. To gain knowledge, students should not be distracted and waste time looking for comfortable tables or chairs. Each office is initially equipped with the necessary equipment and items that are used for studying. However, they strictly comply with current standards and regulations, which are prescribed in order to achieve maximum safety and comfort. The size of desks and furniture in the school with markings according to SanPiN, which describes in detail the necessary data and indicators, can help with this. Number of impressions: 55378
SanPin for primary school material (grade 1) on the topic
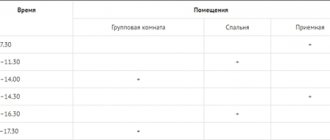
| Sanitary and epidemiological requirements for the conditions and organization of training in educational institutions |
4.27. Washbasins are installed in primary school premises………….
The installation of sinks in classrooms should be provided, taking into account the height and age characteristics of students: at a height of 0.5 m from the floor to the side of the sink for students in grades 1 - 4 and at a height of 0.7 - 0.8 m from the floor to the side of the sink for students
5.3. The main type of student furniture for students of the first stage of education should be a school desk, equipped with a tilt regulator for the surface of the working plane. When learning to write and read, the inclination of the working surface of the school desk plane should be 7 - 15. The front edge of the seat surface should extend beyond the front edge of the working plane of the desk by 4 cm for desks number 1, by 5 - 6 cm for desks number 2 and 3, and by 7 - 8 cm for desks number 4.
The dimensions of educational furniture, depending on the height of students, must correspond to the values given in Table 1.
Table 1
Furniture dimensions and markings
| Furniture numbers according to GOST standards 11015-93 11016-93 | Growth group (in mm) | Height above the floor of the table edge facing the student according to GOST 11015-93 (in mm) | Marking color | Height above the floor of the front edge of the seat according to GOST 11016-93 (in mm) |
| 1000 -1150 | 460 | Orange | 260 | |
| 1150 — 1300 | 520 | Violet | 300 | |
| 1300 — 1450 | 580 | Yellow | 340 | |
| 1450 — 1600 | 640 | Red | 380 | |
| 1600 — 1750 | 700 | Green | 420 | |
| Over 1750 | 760 | Blue | 460 |
A combined option of using different types of student furniture (desks, desks) is allowed.
5.4. To select educational furniture according to the height of students, its color marking is made, which is applied to the visible side outer surface of the table and chair in the form of a circle or stripes.
5.5. Desks (tables) are arranged in classrooms by numbers: smaller ones are closer to the blackboard, larger ones are further away. For children with hearing impairment, desks should be placed in the first row.
It is recommended that children with visual impairments be seated on the desks closest to the blackboard.
Children who often suffer from acute respiratory infections, sore throats, and colds should be seated further from the outer wall.
At least twice during the academic year, students sitting in the outer rows, rows 1 and 3 (with a three-row arrangement of desks), are changed places without disturbing the furniture’s suitability for their height.
In order to prevent postural disorders, it is necessary to cultivate the correct working posture in students from the first days of attending classes in accordance with the recommendations of Appendix 1 of these sanitary rules.
5.6. When equipping classrooms, the following passage dimensions and distances in centimeters are observed:
— between rows of double tables — at least 60;
- between a row of tables and the outer longitudinal wall - at least 50 - 70;
- between a row of tables and an internal longitudinal wall (partition) or cabinets standing along this wall - at least 50;
- from the last tables to the wall (partition) opposite the blackboard - at least 70, from the back wall, which is the outer wall - 100;
- from the demonstration table to the training board - at least 100;
- from the first desk to the blackboard - at least 240;
— the greatest distance from the student’s last place from the blackboard — 860;
— the height of the lower edge of the teaching board above the floor is 70 — 90;
— the distance from the chalkboard to the first row of tables in offices with a square or transverse configuration with a four-row arrangement of furniture is at least 300.
The visibility angle of the board from the edge of the board 3.0 m long to the middle of the student’s extreme seat at the front table must be at least 35 degrees for students of the 2nd - 3rd stages of education and at least 45 degrees for students of the 1st stage of education.
The place of study furthest from windows should not be further than 6.0 m.
In general educational institutions of the first climatic region, the distance of tables (desks) from the outer wall must be at least 1.0 m.
When installing desks in addition to the main student furniture, they are located behind the last row of tables or the first row from the wall opposite the light-carrying one, in compliance with the requirements for the size of passages and distances between equipment.
This furniture arrangement does not apply to classrooms equipped with interactive whiteboards.
In newly constructed and reconstructed buildings of general education institutions, it is necessary to provide a rectangular configuration of classrooms and classrooms with student desks located along the windows and left-side natural lighting.
5.7. Blackboards (using chalk) must be made of materials that have high adhesion to materials used for writing, can be easily cleaned with a damp sponge, be wear-resistant, have a dark green color and an anti-reflective coating.
Chalkboards should have trays for retaining chalk dust, storing chalk, rags, and a holder for drawing supplies.
When using a marker board, the color of the marker should be contrasting (black, red, brown, dark tones of blue and green).
It is allowed to equip classrooms and classrooms with interactive whiteboards that meet hygienic requirements. When using an interactive whiteboard and a projection screen, it is necessary to ensure its uniform illumination and the absence of high-brightness light spots.
6.2. The air temperature, depending on the climatic conditions in classrooms and offices, psychologist and speech therapist offices, laboratories, assembly hall, dining room, recreation, library, lobby, wardrobe should be 18 - 24 C; in the gym and rooms for sectional classes, workshops - 17 - 20 C; bedroom, playrooms, premises of preschool education departments and school boarding schools - 20 - 24 C; ….
To control the temperature regime, classrooms and classrooms must be equipped with household thermometers.
6.6. Educational rooms are ventilated during breaks, and recreational rooms are ventilated during lessons. Before classes start and after they end, it is necessary to carry out cross-ventilation of classrooms. The duration of through ventilation is determined by weather conditions, wind direction and speed, and the efficiency of the heating system. The recommended duration of through ventilation is given in Table 2.
table 2
Recommended duration of cross-ventilation of classrooms depending on the outside air temperature
| Outside temperature С0 | Duration of room ventilation (min) | |
| In small changes | During big breaks and between shifts | |
| From + 10 to +6 | 4-10 | 25-35 |
| From +5 to 0 | 3-7 | 20-30 |
| From 0 to -5 | 2-5 | 15-25 |
| -5 to -10 | 1-3 | 10-15 |
| Below - 10 | 1-1,5 | 5-10 |
VII. Requirements for natural and artificial lighting
7.1. Daylight.
7.1.1. All educational premises must have natural lighting in accordance with the hygienic requirements for natural, artificial, and combined lighting of residential and public buildings.
7.1.3. In classrooms, natural left-side lighting should be designed. When the depth of classrooms is more than 6 m, it is necessary to install right-side lighting, the height of which must be at least 2.2 m from the floor.
The direction of the main light flux in front and behind the students is not allowed.
7.1.7. The windows of classrooms should be oriented to the southern, southeastern and eastern sides of the horizon. The windows of drawing and painting rooms, as well as the kitchen room, can be oriented towards the northern sides of the horizon. The orientation of computer science classrooms is north, northeast.
7.1.8. Light openings in classrooms, depending on the climate zone, are equipped with adjustable sun-shading devices (tilt-and-turn blinds, fabric curtains) with a length not lower than the level of the window sill.
It is recommended to use curtains made from light-colored fabrics that have a sufficient degree of light transmission and good light-diffusing properties, which should not reduce the level of natural light. The use of curtains (curtains), including curtains with lambrequins, made of polyvinyl chloride film and other curtains or devices that limit natural light, is not permitted.
When not in use, curtains must be placed in the walls between the windows.
7.1.9. To rationally use daylight and uniformly illuminate classrooms, you should:
- do not paint over window glass;
- do not place flowers on window sills; they are placed in portable flower boxes 65 - 70 cm high from the floor or hanging flower pots in the walls between the windows;
- Clean and wash glass as it gets dirty, but at least 2 times a year (autumn and spring).
The duration of insolation in classrooms and classrooms must be continuous, with a duration of at least:
— 2.5 hours in the northern zone (north of 58 degrees N);
- 2.0 hours in the central zone (58 - 48 degrees N);
— 1.5 hours in the southern zone (south of 48 degrees N).
.2. Artificial lighting
7.2.1. In all premises of a general education institution, levels of artificial illumination are provided in accordance with the hygienic requirements for natural, artificial, and combined lighting of residential and public buildings.
7.2.2. In classrooms, the general lighting system is provided by ceiling lamps. Fluorescent lighting is provided using lamps according to the color spectrum: white, warm white, natural white.
Lamps used for artificial lighting of classrooms must provide a favorable distribution of brightness in the field of view, which is limited by the discomfort indicator (Mt). The discomfort index of a general lighting lighting installation for any workplace in a classroom should not exceed 40 units.
7.2.3. Fluorescent lamps and incandescent lamps should not be used in the same room for general lighting.
7.2.4. In classrooms, classrooms, laboratories, illumination levels must comply with the following standards: on desktops - 300 - 500 lux, in technical drawing and drawing rooms - 500 lux, in computer science classrooms on tables - 300 - 500 lux, on a blackboard - 300 - 500 lux, in assembly and sports halls (on the floor) - 200 lux, in recreation (on the floor) - 150 lux.
When using computer technology and the need to combine the perception of information from the screen and writing in a notebook, the illumination on students’ desks should be at least 300 lux.
7.2.5. A general lighting system should be used in classrooms. Lamps with fluorescent lamps are located parallel to the light-carrying wall at a distance of 1.2 m from the outer wall and 1.5 m from the inner wall.
7.2.6. A blackboard that does not have its own glow is equipped with local lighting - spotlights designed to illuminate blackboards.
It is recommended to place the lamps 0.3 m above the top edge of the board and 0.6 m towards the classroom in front of the board.
7.2.7. When designing an artificial lighting system for classrooms, it is necessary to provide for separate switching of lamp lines.
7.2.8. For the rational use of artificial light and uniform illumination of classrooms, it is necessary to use finishing materials and paints that create a matte surface with reflection coefficients: for the ceiling - 0.7 - 0.9; for walls - 0.5 - 0.7; for the floor - 0.4 - 0.5; for furniture and desks - 0.45; for chalkboards - 0.1 - 0.2.
It is recommended to use the following paint colors: for ceilings - white, for walls of classrooms - light tones of yellow, beige, pink, green, blue; for furniture (cabinets, desks) - the color of natural wood or light green; for chalkboards - dark green, dark brown; for doors, window frames - white.
7.2.9. It is necessary to clean the lighting fixtures of the lamps as they become dirty, but at least 2 times a year, and promptly replace burnt-out lamps.
7.2.10. Faulty, burnt-out fluorescent lamps are collected in a container in a specially designated room and sent for disposal in accordance with current regulations.
X. Hygienic requirements for the educational process
10.1. The optimal age for starting school is no earlier than 7 years. Children aged 8 or 7 years of age are accepted into 1st grade. Admission of children in the 7th year of life is carried out when they reach the age of at least 6 years 6 months by September 1 of the school year.
The class size, with the exception of compensatory training classes, should not exceed 25 people.
10.2. Education of children under 6 years 6 months at the beginning of the school year should be carried out in a preschool educational institution or in a general education institution in compliance with all hygienic requirements for the conditions and organization of the educational process for preschool children.
10.3. To prevent overwork of students, it is recommended to provide for an even distribution of periods of study time and vacations in the annual calendar curriculum.
10.4. Classes should begin no earlier than 8 o'clock. Conducting zero lessons is not allowed.
In institutions with in-depth study of individual subjects, lyceums and gymnasiums, training is carried out only in the first shift.
In institutions operating in two shifts, training of 1st, 5th, final 9th and 11th grades and compensatory education classes should be organized in the first shift.
Studying in 3 shifts in general education institutions is not allowed.
10.5. The number of hours allocated for students to master the curriculum of a general education institution, consisting of a compulsory part and a part formed by participants in the educational process, should not in total exceed the value of the weekly educational load.
The amount of weekly educational load (number of training sessions), implemented through classroom and extracurricular activities, is determined in accordance with Table 3.
Table 3
Hygienic requirements for maximum weekly educational loads
| Classes | Maximum permissible weekly workload in academic hours | |
| With a 6-day week, no more | With a 5-day week, no more | |
| 1 | — | 21 |
| 2-4 | 26 | 23 |
10.6. The educational weekly load must be evenly distributed during the school week, while the volume of the maximum permissible load during the day should be:
- for 1st grade students should not exceed 4 lessons and 1 day a week - no more than 5 lessons due to a physical education lesson;
- for students in grades 2 - 4 - no more than 5 lessons, and once a week 6 lessons due to a physical education lesson with a 6-day school week;
The lesson schedule is compiled separately for compulsory and elective classes. Optional classes should be scheduled on days with the fewest required classes. It is recommended to take a break of at least 45 minutes between the start of extracurricular activities and the last lesson.
10.7. The lesson schedule is drawn up taking into account the daily and weekly mental performance of students and the scale of difficulty of academic subjects (Appendix 3 of these sanitary rules).
10.8. When drawing up a lesson schedule, you should alternate subjects of varying complexity throughout the day and week: for students of the first stage of education, basic subjects (mathematics, Russian and foreign languages, natural history, computer science) should be alternated with lessons in music, fine arts, labor, physical education…….
For 1st grade students, the most difficult subjects should be taught in the 2nd lesson; 2 - 4 classes - 2 - 3 lessons; for students in grades 5 - 11 in lessons 2 - 4.
In primary grades, double lessons are not conducted.
There should not be more than one test during the school day. Tests are recommended to be carried out in lessons 2–4.
10.9. The duration of the lesson (academic hour) in all classes should not exceed 45 minutes, with the exception of 1st grade, in which the duration is regulated by paragraph 10.10 of these sanitary rules, and the compensating class, the duration of the lesson in which should not exceed 40 minutes.
The density of students' educational work in lessons in core subjects should be 60 - 80%.
10.10. Training in 1st grade is carried out in compliance with the following additional requirements:
— training sessions are conducted over a 5-day school week and only during the first shift;
- use of a “stepped” teaching mode in the first half of the year (in September, October - 3 lessons per day of 35 minutes each, in November - December - 4 lessons of 35 minutes each; January - May - 4 lessons of 45 minutes each );
— it is recommended to organize a dynamic break lasting at least 40 minutes in the middle of the school day;
— for those attending an extended day group, it is necessary to organize daytime sleep (at least 1 hour), 3 meals a day and walks;
— training is carried out without scoring students’ knowledge and homework;
— additional week-long holidays in the middle of the third quarter in the traditional mode of education.
10.11. To prevent overwork and maintain an optimal level of performance during the week, students should have a light school day on Thursday or Friday.
10.12. The duration of breaks between lessons is at least 10 minutes, long breaks (after the 2nd or 3rd lessons) - 20 - 30 minutes. Instead of one big break, it is allowed after the 2nd and 3rd lessons to have two breaks of 20 minutes each.
It is recommended to organize recess outdoors. For this purpose, when conducting a daily dynamic break, it is recommended to increase the duration of the long break to 45 minutes, of which at least 30 minutes are allocated for organizing motor-active activities of students on the institution’s sports ground, in the gym or in recreation.
10.17. In order to prevent fatigue, impaired posture and vision of students, physical education and eye exercises should be carried out during lessons (Appendix 4 and Appendix 5 of these sanitary rules).
10.18. It is necessary to alternate different types of learning activities during the lesson (with the exception of tests). The average continuous duration of various types of educational activities of students (reading from paper, writing, listening, questioning, etc.) in grades 1 - 4 should not exceed 7 - 10 minutes......
The duration of continuous use of technical teaching aids in the educational process is established according to Table 5.
Table 5
Duration of continuous use of technical teaching aids in lessons
| Classes | Continuous duration (min.) no more | |||||
| View statistical images on whiteboards and reflective displays | Watching TV | View dynamic images on whiteboards and bounce screens | Working with images on an individual computer monitor and keyboard | Listenable audio recordings | Listening to audio with headphones | |
| 1 — 2 | 10 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 20 | 10 |
| 3 — 4 | 15 | 20 | 20 | 15 | 20 | 15 |
After using technical teaching aids related to visual load, it is necessary to carry out a set of exercises to prevent eye fatigue (Appendix 5), and at the end of the lesson - physical exercises to prevent general fatigue (Appendix 4).
10.20. To satisfy the biological need for movement, regardless of the age of students, it is recommended to conduct at least 3 physical education lessons per week, provided for in the amount of the maximum permissible weekly load. It is not allowed to replace physical education lessons with other subjects.
10.21. To increase the motor activity of students, it is recommended to include subjects of a motor-active nature (choreography, rhythm, modern and ballroom dancing, training in traditional and national sports games) in the curricula for students.
10.22. In addition to physical education lessons, the physical activity of students in the educational process can be ensured through:
— physical education minutes in accordance with the recommended set of exercises (Appendix 4);
— organized outdoor games during breaks;
— sports hour for children attending an extended day group;
- extracurricular sports activities and competitions, school-wide sports events, health days;
— independent physical education in sections and clubs.
10.25. During labor classes provided for in the educational program, tasks of different nature should be alternated. You should not perform one type of activity during the entire period of independent work in a lesson.
10.30. The amount of homework (in all subjects) should be such that the time required to complete it does not exceed (in astronomical hours): in grades 2 - 3 - 1.5 hours, in grades 4 - 5 - 2 hours.
10.32. The weight of a daily set of textbooks and writing materials should not exceed: for students of 1st - 2nd grades - more than 1.5 kg, 3rd - 4th grades - more than 2 kg...
10.33. In order to prevent poor posture in students, it is recommended that primary school students have two sets of textbooks: one for use in lessons in a general education institution, the second for preparing homework.
Recommendations for education and formation of correct working posture among students
In order to form correct posture and maintain health, it is necessary to educate and form the correct working posture of students at a school desk from the first days of schooling in a general education institution. To do this, it is necessary to devote a special lesson in the first grades.
To form correct posture, it is necessary to provide a workplace for the student with furniture in accordance with his height; teach him to maintain the correct working posture during training sessions, which is the least tiring: sit deeply in a chair, hold his body and head straight; legs should be bent at the hip and knee joints, feet resting on the floor, forearms resting freely on the table.
When placing a student at a desk, the chair is moved under the table so that when leaning on the back, his palm is placed between the chest and the table.
For rational selection of furniture in order to prevent disorders of the musculoskeletal system, it is recommended to equip all classrooms and classrooms with height rulers.
The teacher explains to students how to hold their head, shoulders, arms, and emphasizes that they should not lean their chest on the edge of the desk (table); the distance from the eyes to the book or notebook should be equal to the length of the forearm from the elbow to the end of the fingers. The hands lie freely, not pressed against the table, the right hand and the fingers of the left rest on the notebook. Both legs rest with their entire feet on the floor.
When mastering writing skills, the student leans on the back of the desk (chair) with his lower back; when the teacher explains, he sits more freely, leaning on the back of the desk (chair) not only with the sacro-lumbar part of the back, but also with the subscapular part of the back. After explaining and demonstrating the correct sitting position at a desk, the teacher asks the students of the whole class to sit correctly and, going around the class, corrects them if necessary.
The table “Sit Correctly When Writing” should be placed in the classroom so that students always have it before their eyes. At the same time, students need to be shown tables demonstrating defects in posture that arise as a result of incorrect seating. The development of a certain skill is achieved not only by explanation, supported by demonstration, but also by systematic repetition. To develop the skill of correct posture, the teacher must daily monitor the correct posture of students during classes.
The role of the teacher in instilling correct posture in students is especially important during the first three to four years of study in a general education institution, when they develop this skill, as well as in subsequent years of study.
The teacher, in collaboration with parents, can give recommendations on choosing a backpack for textbooks and school supplies: the weight of the backpack without textbooks for students in grades 1 - 4 should be no more than 700 g. In this case, the backpack should have wide straps (4 - 4.5 cm) and sufficient dimensional stability to ensure a tight fit to the student’s back and uniform weight distribution. The material for making backpacks should be light, durable, with a water-repellent coating, easy to clean.
Appendix 3
Hygienic recommendations for lesson schedules
Modern scientific research has established that the biorhythmological optimum of mental performance in school-age children falls within the interval of 10–12 hours. During these hours, the greatest efficiency of assimilation of material is observed at the lowest psychophysiological costs for the body.
Therefore, in the lesson schedule for students of the 1st stage of education, the main subjects should be taught in lessons 2-3, and for students of the P and III levels of education - in lessons 2, 3, 4.
The mental performance of students on different days of the school week is not the same. Its level increases towards the middle of the week and remains low at the beginning (Monday) and at the end (Friday) of the week.
Therefore, the distribution of the teaching load during the week is structured in such a way that its largest volume falls on Tuesday and (or) Wednesday. On these days, the lesson schedule includes subjects that correspond to the highest score on the difficulty scale (Tables 1, 2, 3 of this appendix), or with an average score and the lowest score on the difficulty scale, but in greater quantities than on other days of the week. Presentation of new material and tests should be carried out in 2-4 lessons in the middle of the school week.
Subjects that require a lot of time to prepare at home should not be grouped together on the same day.
When drawing up a lesson schedule for primary, middle and high school students, you must use tables 1 – 3, in which the difficulty of each academic subject is ranked in points.
It is recommended to include physical education classes among the last lessons. After physical education lessons there are no lessons with written assignments or tests.
With a correctly drawn up lesson schedule, the highest number of points per day based on the sum of all subjects should fall on Tuesday and (or) Wednesday.
Table 1.
Scale of subject difficulty for grades 1-4
| General subjects | Number of points (difficulty rank) |
| Mathematics | 8 |
| Russian (national foreign language) | 7 |
| Natural history, computer science | 6 |
| Russian (national literature) | 5 |
| History (4 classes) | 4 |
| Drawing and music | 3 |
| Work | 2 |
| Physical Culture | 1 |
Appendix 4 to SanPiN 2.4.2.2821-10
Recommended set of exercises
physical education minutes (FM)
Training sessions that combine mental, static, and dynamic loads on individual organs and systems and on the entire body as a whole require physical education minutes (hereinafter referred to as FM) during lessons to relieve local fatigue and FM of the general impact.
FM to improve cerebral circulation:
1. Starting position (hereinafter - i.p.) - sitting on a chair. 1 - 2 - move your head back and smoothly tilt it back, 3 - 4 - tilt your head forward, do not raise your shoulders. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is slow.
2. I.p. - sitting, hands on the belt. 1 - turn the head to the right, 2 - i.p., 3 - turn the head to the left, 4 - i.p. Repeat 6 - 8 times. The pace is slow.
3. I.p. - standing or sitting, hands on the belt. 1 - swing your left arm over your right shoulder, turn your head to the left. 2 - IP, 3 - 4 - the same with the right hand. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is slow.
FM to relieve fatigue from the shoulder girdle and arms:
1. I.p. - standing or sitting, hands on the belt. 1 - right hand forward, left hand up. 2 - change hand positions. Repeat 3-4 times, then relax down and shake your hands, tilt your head forward. The pace is average.
2. I.p. - standing or sitting, with the back of your hands on your belt. 1 - 2 - bring your elbows forward, tilt your head forward, 3 - 4 - elbows back, bend over. Repeat 6 - 8 times, then hands down and shake relaxed. The pace is slow.
3. I.p. - sitting, hands up. 1 - clench your hands into a fist, 2 - unclench your hands. Repeat 6 - 8 times, then relax your arms down and shake your hands. The pace is average.
FM to relieve fatigue from the torso:
1. I.p. - stand with your feet apart, hands behind your head. 1 - sharply turn the pelvis to the right. 2 - sharply turn the pelvis to the left. During turns, leave the shoulder girdle motionless. Repeat 6 - 8 times. The pace is average.
2. I.p. - stand with your feet apart, hands behind your head. 1 - 5 - circular movements of the pelvis in one direction, 4 - 6 - the same in the other direction, 7 - 8 - arms down and shake your hands in a relaxed manner. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is average.
3. I.p. - stand with legs apart. 1 - 2 - bend forward, the right hand slides down along the leg, the left, bending, along the body up, 3 - 4 - IP, 5 - 8 - the same in the other direction. Repeat 6 - 8 times. The pace is average.
General impact FM consists of exercises for different muscle groups, taking into account their tension during activity.
A set of FM exercises for students of the first stage of education in lessons with elements of writing:
1. Exercises to improve cerebral circulation. I.p. - sitting, hands on the belt. 1 - turn the head to the right, 2 - i.p., 3 - turn the head to the left, 4 - i.p., 5 - smoothly tilt the head back, 6 - i.p., 7 - tilt the head forward. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is slow.
2. Exercises to relieve fatigue from the small muscles of the hand. I.p. - sitting, arms raised up. 1 - clench your hands into a fist, 2 - unclench your hands. Repeat 6 - 8 times, then relax your arms down and shake your hands. The pace is average.
3. Exercise to relieve fatigue from the muscles of the torso. I.p. - stand with your feet apart, hands behind your head. 1 - sharply turn the pelvis to the right. 2 - sharply turn the pelvis to the left. During turns, leave the shoulder girdle motionless. Repeat 4 - 6 times. The pace is average.
4. Exercise to mobilize attention. I.p. - standing, arms along the body. 1 - right hand on the belt, 2 - left hand on the belt, 3 - right hand on the shoulder, 4 - left hand on the shoulder, 5 - right hand up, 6 - left hand up, 7 - 8 - clapping hands above the head, 9 - put your left hand on your shoulder, 10 - your right hand on your shoulder, 11 - your left hand on your belt, 12 - your right hand on your belt, 13 - 14 - clap your hands on your hips. Repeat 4 - 6 times. Tempo - 1 time slow, 2 - 3 times - medium, 4 - 5 - fast, 6 - slow.
Appendix 5 to SanPiN 2.4.2.2821-10
Recommended set of eye gymnastics exercises
1. Blink quickly, close your eyes and sit quietly, slowly counting to 5. Repeat 4 - 5 times.
2. Close your eyes tightly (count to 3, open them and look into the distance (count to 5). Repeat 4 - 5 times.
3. Extend your right arm forward. Follow with your eyes, without turning your head, the slow movements of the index finger of your outstretched hand to the left and right, up and down. Repeat 4 - 5 times.
4. Look at the index finger of your outstretched hand for the count of 1 - 4, then move your gaze into the distance for the count of 1 - 6. Repeat 4 - 5 times.
5. At an average pace, make 3-4 circular movements with your eyes to the right side, and the same amount to the left side. Having relaxed your eye muscles, look into the distance while counting 1 - 6. Repeat 1 - 2 times.
Extracurricular activities.
Extracurricular activities are carried out in the form of excursions, clubs, sections, Olympiads, competitions, etc.
The duration of classes depends on age and type of activity. The duration of activities such as reading, music lessons, drawing, modeling, needlework, quiet games should be no more than 50 minutes a day for students in grades 1-2, and no more than one and a half hours a day for other grades. In music classes, it is recommended to use elements of rhythm and choreography more widely. Watching TV shows and movies should not be done more than twice a week, with viewing duration limited to 1 hour for students in grades 1–3 and 1.5 for students in grades 4–8.
It is recommended to use general school premises for organizing various types of extracurricular activities: reading, assembly and sports halls, a library, as well as premises of nearby cultural centers, children's leisure centers, sports facilities, stadiums.
Nutrition.
Properly organized and rational nutrition is the most important health factor. When organizing an extended day in a general education institution, three meals a day must be provided for students: breakfast - at the second or third break during school hours; lunch - during extended day stay at 13-14 hours, afternoon snack - at 16-17 hours.
Appendix 7
Recommendations for conducting physical education classes depending on temperature and wind speed in some climatic zones of the Russian Federation outdoors in the winter.
| Climate zone | Age of students | Air temperature and wind speed at which outdoor activities are allowed | |||
| No wind | At wind speed 5 m/s | At wind speed 6-10m/s | When the wind speed is more than 10 m/s | ||
| Northern part of the Russian Federation (Krasnoyarsk Territory, Omsk Region, etc.) | Up to 12 years | -10 -11 оС | -6 -7 оС | -3 -4 оС | Classes are not held |