What is an appeal?
There are 2 concepts of appeal: it is considered as a procedure for appealing a court decision or as a document initiating it. Considering the topic, it is necessary to focus on the 2nd definition.
An appeal is a document drawn up according to certain rules, in which the applicant demands to cancel or change a court decision of the first instance that has not entered into legal force. It has a number of distinctive features.
- An appeal is only possible against a decision of the first instance court that has not taken effect.
- The circle of applicants is limited to the plaintiff and the defendant. In some cases, an appeal to the court of the next instance can be sent by a third party who makes independent claims on the subject of the dispute or by a prosecutor acting in defense of a number of entities.
- The addressee of the complaint is the higher court. This could be any institution of Themis. The only exception is magistrates.
- Special rules are established regarding the content, format and timing of the referral (Chapter 34 of the APC, Chapter 39 of the Code of Civil Procedure).
This is also important to know:
How to challenge the cadastral value of real estate: apartment, land plot
All of the above features are mandatory.
When can you appeal a court decision?
The stage of appealing an act that has not entered into force is provided for in all types of legal proceedings. An appeal is possible:
- in criminal proceedings;
- when considering cases of administrative offenses;
- during civil proceedings.
- as part of the consideration of the case by arbitration.
This is also important to know:
Characteristics of the driver from the place of work
Before filing an appeal as part of the consideration of the case, you should study the rules established by the relevant code. They take into account the specifics of each type of legal proceedings, therefore a number of rules for drafting, execution and direction have significant differences.
find_in_page
Articles on the topic
(click to open)
Additionally, it is recommended to know how to write an application to Rospotrebnadzor.
Appeal in an administrative case
The rules governing the procedure for challenging a court decision in an administrative case are established by Section 6 of the CAS RF. An appeal is filed within one month from the date of adoption of the full text of the contested act.
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
If during the final hearing only the operative part of the document was read (the judge imposed the punishment without reading his arguments), the period of challenge will begin to count from the date indicated in the full text.
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question
There are other deadlines.
- Decisions on the deportation of foreigners, in cases related to administrative supervision, forced hospitalization in psychiatric institutions, as well as cases of dissolution of municipal bodies can be challenged within 10 days.
- If the adopted act concerns issues of conducting election campaigns and voting, the appeal period is 5 days.
- The appeal is filed within 15 days when the decision was made in a simplified manner.
The law allows for the transfer of a document to the court office, as well as its sending by mail (the date of circulation will be the stamp on the envelope made by the employee who received the letter). Another way is to approach the court through its online portal.

How to submit documents?
According to paragraph 1 of Art. 260 Federal Law No. 95, documents can be submitted in two formats:
- In writing
. The package of papers can be submitted directly in person to the court office or by registered mail, in which case you will need to make an inventory of the attachment and receive notification of the successful delivery of the letter. - Electronic
_ All papers can be sent through the official website of the arbitration court. This was determined by the resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court No. 80 of November 8, 2013.
It is necessary to send a complaint with a package of papers not only to the court, but also to all persons participating in the trial. According to paragraph 3 of Art. 260 Federal Law No. 95, this can be done by registered mail with receipt of receipt or by personal delivery with a receipt.
How to write an appeal against a court decision, sample
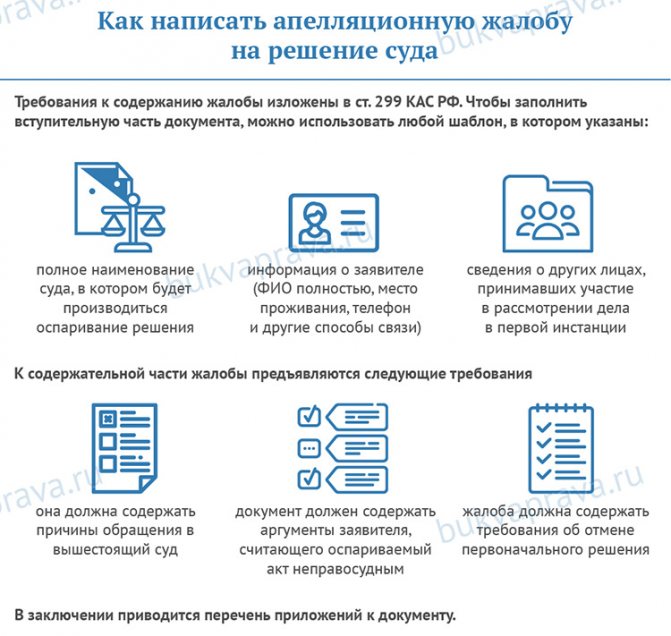
The requirements for the content of the complaint are set out in Art. 299 CAS RF. You can use any template to fill out the introductory part of the complaint.
Fact
Sample appeal in an administrative case

The initial part of the document states:
- full name of the court in which the decision will be challenged;
- information about the applicant (full name, place of residence, telephone and other means of communication);
- information about other persons who took part in the consideration of the case in the first instance.
This is also important to know:
Petition: sample, how to write correctly
The following is the essence of the complaint. Each case has its own characteristics, so a document template will not always be useful. Before filing an appeal against a court decision, it is advisable to consult with a lawyer who specializes in such cases. The following requirements apply to the content of the complaint:
- it must contain the reasons for appealing to a higher court;
- the document must contain the arguments of the applicant who considers the contested act to be unjust;
- the complaint must contain demands to have the original decision reversed.
Finally, a list of appendices to the document is provided.
How to appeal a court decision
How to file an appeal in a criminal case
The procedure for challenging sentences has a number of features. The procedure for filing an appeal in a crime case is established by Chapter 45.1 of the Code of Criminal Procedure of the Russian Federation.
- The document is sent directly to the court of the next instance.
- You can file an appeal against the court decision within 10 days after the verdict is passed. If the applicant is in custody, then this period begins to be calculated from the moment he is given a copy of the act.
The price of errors and inaccuracies in a document may be the freedom of a citizen or his property well-being. For this reason, it is recommended to involve a lawyer who is well-established in such cases in drafting and filing the complaint.

How to write an appeal against a court decision in a civil case
Appeals against judicial acts in civil cases that have not entered into force are provided for in Chapter 39 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. The law establishes the following features of challenging decisions:
- the document is submitted through the court that made the original decision;
- An appeal can be filed within 1 month after the full text of the act is prepared.
This is also important to know:
Article for libel and insult to personality in 2021
The requirements for the content of the document are similar to the rules relating to administrative proceedings. The complaint must contain information about the authority considering it, the parties, the applicant’s arguments and his demands, as well as a list of accompanying materials (documents, receipts for payment of state fees, etc.).

Filing an appeal in arbitration cases
Challenging decisions in civil cases in the economic sphere is regulated by Chapter 34 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation. Unlike civil proceedings, the arbitration process involves sending a document directly to the appellate court.
The general period for challenging an act is 30 days from the date of production of its full text. The appeal period will be limited to 15 days if the decision was made in a summary manner.
Free legal consultation We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Call: 8 800 511-39-66
Additionally, you can study information about what the article is for libel.
Free legal consultation
We will answer your question in 5 minutes!
Ask a Question

Explanatory note for drawing up an appeal.
An appeal may be filed within a month after the arbitration court of first instance makes the appealed decision, unless a different period is established by the Arbitration Procedural Code of the Russian Federation.
Other deadlines are established for filing a complaint in cases related to administrative proceedings and in some other cases. The content of the appeal must meet the requirements in accordance with Art. 259, 260 Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, Art. 333 Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. The task of the appellate instance is to consider the disputed legal relationship on its merits, taking into account already considered and new evidence. When presenting new evidence in the appeal, the applicant must justify the reasons for its failure to provide it in the court of first instance. Economic tasks that can be solved by participants include the protection of violated and disputed rights of persons engaged in entrepreneurial and economic activities. Procedural tasks: familiarize yourself with the case materials, provide evidence, give explanations to the arbitration court. The defendant has the right to admit the claim in whole or in part. The parties can come to an amicable agreement.
The appeal is made in writing and must contain the following information:
- Full name of the authority in which the appeal of the court decision is expected, for example, the Seventeenth Arbitration Court of Appeal, 614068 Perm st. Pushkina, 112;
- Full details of the parties who took part in the trial (for legal entities - full name of the organization, tax identification number, OGRN, legal address, contact numbers; for individuals - last name, first name, patronymic, passport details, address and contact numbers);
- The name of the judicial authority that issued the judicial act (which served as the basis for appealing the court decision);
- Type and date of adoption of the judicial act (decision, ruling), for example, “Appeal against the ruling dated December 24, 2012 in case A60-1234/2012 of the Arbitration Court of the Sverdlovsk Region”
- Subject of dispute;
- Applicant's requirements;
- The applicant's arguments;
- Links to regulations (grounds for appealing a court decision);
- The scope of appealing the court decision (the applicant demands the cancellation of the court decision in whole or in part).
Learn more about where to start and how to write an appeal.
is set out on the page Methodology for writing an appeal.
In the upper right corner of the appeal to the court document the following is indicated:
• Name of the court to which the complaint is addressed, its address;
• The name of the person participating in the case, on whose behalf the complaint is being filed, his location. FULL NAME. applicant, his position
Then, in the middle of the sheet, it is advisable to write “Appeal” and indicate the details of the judicial act (on the decision, court ruling) that is being appealed, the date of its adoption, the case number.
The main part of the complaint must contain arguments, i.e. reasons why you consider the judge’s decision to be illegal. When describing the arguments, it is necessary that they be the basis for canceling or changing the appealed decision, since a decision of the first instance court that is essentially correct will most likely not be canceled for formal reasons alone.
The appeal is accompanied by a list of documents that serve as the evidentiary basis for filing the appeal:
- court decision that is subject to appeal (copy);
- confirmation of sending the appeal to other participants by registered mail with acknowledgment of delivery (postal receipt (check order)
- as well as a receipt for payment of the state duty.
- The appeal must also be accompanied by: an official document confirming the authority of the person who signed the appeal on behalf of the organization (power of attorney, extract from the register, order of the company management, etc.), as well as other documents that are relevant to the appeal.
- extracts from the Unified State Register of Legal Entities in relation to all persons participating in the case
To exercise this right of appeal, it is necessary to have an object and subjects of appeal. The object of the appeal is decisions (including absentee, additional decisions) and rulings of the magistrate that have not entered into legal force. Subjects who have the right of appeal include persons participating in the case (parties, third parties making independent claims on the subject of the dispute, third parties not making independent claims on the subject of the dispute, prosecutor), as well as persons not involved in the case , the question of the rights and obligations of which was resolved by the court of first instance.
An appeal cannot contain claims that have not been previously stated. The existence of this prohibition in the law is explained by the fact that the basis of the appeal is the rule of “double criminality”. This means that the same case must be considered twice: the first time - in the court of first instance; the second time - in the court of appeal (clause 7 of Article 268 of the Arbitration Procedure Code, clause 2 of Article 322 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
An appeal is filed through the court that adopted the appealed judicial act (decision, decree, etc.).
Deadline for filing an appeal
The period for filing an appeal will be 10 days if:
- the case concerns bringing the applicant to administrative liability;
- the subject of consideration was a document on bringing to administrative responsibility issued by the executive body;
- if the decision concerns forcing the convening of a general meeting of the organization’s participants.
The document can be transmitted through the office, sent by mail or through the court website.

Time limits for consideration of an appeal
The law limits the period within which a complaint must be considered. For administrative cases, it is 2 months from the date of receipt of materials. If the appeal is considered by the Supreme Court, the period is 3 months.
A similar procedure is established for civil cases.
A 2-month limitation is provided for when considering appeals in the arbitration process. The law allows for the possibility of extending this period to 6 months if this is due to a large number of participants or other circumstances that make the case considered complex.
This is also important to know:
How to find out a court decision in the Russian Federation by last name in 2021
Complaints filed in connection with convictions are subject to review within a 30-day period. If the Supreme Court is the appellate authority, the period for completing the procedure is extended to 45 days.

Consideration of the case on appeal
The Moscow City Court is given two months to consider the appeal. The parties are notified in advance of the date and location of the meeting.
If the parties did not take care to notify the court in advance about the impossibility of participating in the court hearing and postponing the case, then the consideration takes place without them.
The appellate court will make an appeal ruling in the absence of the parties. Of course, there must be good reasons for the non-appearance of persons participating in the case.
When considering an appeal in civil cases, the court has the right to make the following decisions:
:
- Leaving the complaint unsatisfied.
- Cancellation of the decision made by the court of first instance and the issuance of a new decision in the case. It is possible to cancel the entire act or part of it.
- Cancellation of the decision and termination of the proceedings.
- Leaving a complaint without consideration due to missing the deadline provided by law for an appeal.
If you disagree with the outcome of the appeal, you can file a cassation appeal with a higher court within six months.
State duty when filing an appeal
One of the conditions for challenging a court decision is the payment of the fee required by law. The state fee for an appeal is established in Chapter 25.3 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
Its size is not related to the sphere of legal proceedings, but to a specific institution of themis. The state fee for filing an appeal, which is sent to the courts of general jurisdiction, is 150 rubles for citizens and 3,000 rubles if the decision is challenged by a legal entity.
If the case relates to economic disputes, then different rules will apply. The state fee for an appeal to the arbitration court will be 3,000 rubles, regardless of the applicant’s status.

Before challenging any decision, you must ensure that all required documents are available. It is also important to determine whether the state duty has been paid correctly. An appeal against a decision of an arbitration court or other institution will be left without progress if the required payment is not transferred in accordance with the details.
The arbitration court of appeal may return the appeal if it finds that:
- the complaint was filed by a person who does not have the right to appeal a judicial act in the manner of appellate proceedings ;
- the complaint was filed against a judicial act, which, in accordance with the Arbitration Procedural Code, cannot be appealed through the appellate procedure ;
- the complaint was filed after the expiration of the deadline for filing an appeal established in the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation, and does not contain a request for its restoration or the restoration of the missed deadline for filing an appeal was refused;
- before the decision was made to accept the appeal for court proceedings, the person who filed the complaint received a petition for its return ;
- the circumstances that served as the basis for leaving the complaint without progress within the period established in the court ruling.
- The arbitration court of appeal also returns the complaint if
the request for a deferment, installment payment of the state fee or a reduction in its amount is rejected
On the return of the appeal, the arbitration court issues a ruling, which indicates the grounds for returning the appeal , and resolves the issue of returning the state duty .
The return of the appeal does not prevent the repeated filing of
the appeal with the arbitration court in the general manner after the elimination of the circumstances that served as the basis for its return .
The appellate instance leaves the complaint without progress if it is filed in violation of the requirements established by Article 260 of the Arbitration Procedural Code (Part 1 of Article 263 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation). In this case, the court allots a certain time to the applicant in order for him to eliminate the identified shortcomings. If the applicant does not do this, the complaint will be returned.
The reason for leaving a complaint without progress is often the lack of documents that, by law, must be attached to it. Thus, the law requires that the complainant send to the rest of the persons participating in the case a copy of it and other documents that they do not have, by post with acknowledgment of receipt (Part 3 of Article 260 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation). As evidence of the fulfillment of this requirement, the appeal must be accompanied by a postal receipt, an inventory of the attachment and a notice of sending and delivery of a copy of the complaint. The Court will leave the complaint without progress, even if the documents were sent by registered mail with an inventory of the attachment.
Instead of sending by mail, the applicant may, against receipt, hand over to the person participating in the case copies of the complaint and documents missing from him. This receipt is then attached to the appeal. But in order for the court to accept it as evidence of delivery, it must contain a transcript of the last name, first name, patronymic and position of the person who accepted the documents, as well as text confirming receipt of these documents.
In addition, original documents confirming payment of the state duty or the right to receive benefits for its payment must be attached to the appeal. Moreover, the court will leave the complaint without progress even in the case where the state duty was paid, but according to incorrect details or in an insufficient amount, or there were no marks of the bank (Federal Treasury body) on the payment documents.
Request for deferment or installment payment of the state fee for filing an appeal
Instead of a receipt (payment order) for payment of the state duty, the applicant can submit a petition for a deferment or installment plan for its payment or for a reduction in its amount (clause 2, part 4, article 260 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation). To do this, he must confirm his difficult financial situation. To do this, you can use the following documents.
- Firstly, this is a list of the applicant’s current and other accounts confirmed by the tax authority, indicating the names and addresses of the banks in which they are open. This list includes accounts of branches and representative offices.
- Secondly, this is data confirmed by the bank about the absence of funds in the indicated accounts in the amount necessary to pay the state duty, as well as about the applicant’s debt under writs of execution and payment documents. If in the application the applicant asks for a reduction in the amount of the state duty, then documents on the funds in the account are attached to it.
If the applicant asked for a deferment, installment plan, or reduction of the state fee, but did not attach the mentioned documents to the petition, the court will not leave the appeal without progress and invite the applicant to submit the missing certificates. He will simply return the complaint.
If the applicant eliminates the shortcomings of his complaint in a timely manner (pays the state fee, provides evidence of sending copies of documents to the persons participating in the case, etc.), the court issues a ruling on its acceptance, and the ruling on leaving the complaint without progress is lost. If the applicant does not eliminate the shortcomings, and also if his request to reduce, defer or installment payment of the state duty is rejected, the court returns the appeal to him. Having eliminated the circumstances due to which the court returned the complaint, the applicant can file it again (Part 1.5 of Article 264 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation), of course, if the month-long deadline for appeal is not missed (Article 259 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation).
The complaint must be signed by the executive body of the legal entity or an authorized representative (Part 1 of Article 260 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation). Oddly enough, applicants sometimes have difficulties fulfilling this requirement. For example, the general director of the applicant company went on vacation and the complaint had to be signed by his deputy, who did not have the appropriate power of attorney. Since the deputy is not a body of a legal entity, he can sign an appeal on its behalf only after receiving the appropriate power of attorney signed by the general director (clause 4, part 4, article 260 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation).
Some courts will leave a complaint that is not signed by an authorized representative. But there is another approach, according to which doubts about the authority of the person who signed the complaint are not a reason to leave it without progress. In this case, the head of the company on behalf of which the complaint was filed may declare in court that he approves of the actions of the person who signed the complaint. According to the Plenum of the Supreme Arbitration Court, the appellate instance must invite the applicant to approve the actions of the “signatory” or provide evidence of his authority to appeal (clause 21 of the resolution dated 28.05-09 No. 36 “On the application of the Arbitration Procedural Code of the Russian Federation when considering cases in arbitration court of appeal"). If the applicant does not do this, the appeal is left without consideration (clause 7, part 1, article 148 of the Arbitration Procedure Code of the Russian Federation).
The requirements set out in the ruling on leaving the complaint without progress are considered fulfilled only at the time the documents are received by the court. Therefore, the applicant must send the documents requested by the court in such a way that they arrive directly at the court by the date appointed in the ruling. The deadline for sending documents to the court is confirmed by a postal receipt and a stamp on the envelope. If the court receives these documents after the end of the period allotted in the ruling, it will return the complaint.
Thus, if the applicant submitted the documents required by the court of appeal by mail 1-2 days before the end of the allotted period, this may mean that he actually missed the opportunity to appeal. However, he can submit these documents directly to the court on the last day of the term (which confirmed by a stamp of incoming correspondence). In this case, he is considered to have complied with the requirements of the appellate court on time.
The grounds for termination of appeal proceedings are based on the following grounds:
- A petition for refusal was received from the person who filed the complaint; subsequently, the refusal was accepted;
- The complaint states claims that were not specified for consideration in the court of first instance.
Features of appealing judicial acts during bankruptcy procedures
During bankruptcy proceedings, a number of judicial acts can be appealed. According to Art. 58 of the Bankruptcy Law, a person participating in a bankruptcy case may apply to suspend the bankruptcy case when appealing the following judicial acts:
- decision to declare the debtor bankrupt and to open bankruptcy proceedings;
- decision to refuse to declare the debtor bankrupt;
- determination on the introduction of financial recovery;
- determination on the introduction of external management;
- determination to terminate bankruptcy proceedings;
- a ruling to leave the application for declaring the debtor bankrupt without consideration;
- determination on approval of the settlement agreement.
An appeal against the ruling on the introduction of supervision and the approval of the declared arbitration manager as a temporary manager is possible. Appealing these determinations does not suspend their immediate execution.








