What is a cassation appeal
A cassation appeal is a complaint against a court decision that has entered into legal force.
The cassation instance is intended to correct significant violations of the norms of substantive law or norms of procedural law committed by the courts during the proceedings of a civil case and influencing the outcome of the case, in cases where without their elimination it is impossible to restore and protect the violated rights, freedoms and legitimate interests, as well as the protected law of public interests.
When considering a cassation appeal, the cassation court checks only the legality of court decisions, that is, the correct application and interpretation of the norms of substantive law and norms of procedural law (Part 2 of Article 0 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
| Note! |
| Appeal against a court decision |
Cassation procedure
Before commencing the review, the third instance court assesses whether there are grounds for returning the complaint without consideration. Such grounds may arise if the complaint is written incorrectly. For example, from its contents it is not clear which case needs to be reclaimed from the district court, or the applicant’s details are not indicated.
The return of the complaint will also take place if it was written by an inappropriate person - for example, a complete stranger whose rights are in no way affected by the decision being appealed. In addition, if the one-year deadline for a cassation appeal is missed with a possible turn for the worse (for example, a complaint about the leniency of the sentence), under no circumstances can it be restored (even if there is a good reason) and then the complaint is also returned to the applicant.
If the judge decides that the complaint needs to be returned, he must do so within 10 days from the date it was received by the court.
If all the formalities have been checked and the judge has concluded that it is possible to proceed with the review, the procedure itself begins:
1. The court examines the received complaint and decides whether it is necessary to request the case or material from the court of first instance (after the appeal has made its decision, the case is returned to the district court).
2. If the case is requested (in most cases this happens), the period for consideration of the cassation appeal is calculated from the moment when the case was actually received upon request by the Presidium and is 2 months (in the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation - 3 months). If there is no need to reclaim the case, the period for review is 1 month (in the RF Armed Forces - 2 months)
3. The judge studying the materials makes a decision to transfer the complaint and case materials to the collegium.
Let us recall that review in the cassation sense means the actual study of case documents for compliance with legal requirements. The judge studying the case does not analyze how well-founded the conclusion was made by previous authorities, or how well the conclusion about what happened corresponds to the factual data. The subject of study is only compliance with the Code of Criminal Procedure and the Criminal Code of the Russian Federation.
Therefore, if the case or material does not raise doubts in the judge studying it about the compliance of the decision made with the requirements of legality, transfer to cassation consideration may be refused. A decision is made on this, and the documents attached to the complaint remain in the court of third instance.
The Chairman of the Supreme Court or his deputy may disagree with the refusal and make a decision to transfer the complaint to a cassation hearing. Such cases are extremely rare in practice.
At the same time, neither the deputies nor the Chairman of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation himself has the right to cancel the decision of the judge of the Presidium of the regional court or the judicial collegium of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation to transfer the complaint to the court for review. It is believed that the judge who makes the decision to transfer the case for review allows for the identification of violations of the law in the verdict.
4. Participants in the procedure (the applicant, his defense attorney, as well as the opposite party) are notified of the upcoming date of review. However, their failure to appear is not grounds for postponing the meeting, since it is not considered mandatory. The only exception is the participation of the prosecutor - it is mandatory.
5. Three judges participate in the review procedure, one of whom is the rapporteur, that is, the judge who has fully studied the case and, to a certain extent, has already formed his opinion on the legality of the decisions made.
Each of the three judges has the right to address any document and case, including additionally submitted ones. In this case, the examination of evidence as such is not carried out; the emphasis is only on assessing the court decisions made regarding the correct application of criminal and criminal procedural laws.
Judges carefully study the minutes of previous meetings, compare them with the essence of the sentence or resolution, and evaluate the resolution of legal (procedural) issues arising in the first and second instances.
It is noteworthy that the judge does not have the right to participate in the cassation board if he made a decision to send the case for review.
Court decisions that can be appealed in cassation
The following court decisions that have entered into legal force can be appealed through the cassation procedure:
- decisions, rulings of district courts, garrison military courts, justices of the peace, adopted by them at first instance, court orders;
- appeal rulings made by courts based on the results of consideration of cases on appeal and private complaints, presentations, with the exception of appeal rulings of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation (clauses 4 - 5 of part 2 of Article 391.1 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation);
- rulings made by the courts of appeal, specified in paragraphs 1 and 2 of Article 320.1 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation, on leaving without consideration on the merits of appeals, presentations based on paragraph 4 of Article 328 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation and other rulings;
- decisions of the presidiums of regional and equal courts
2021 update
It should be taken into account that on February 24, 2021, important changes were made to the deadline for cassation appeals, which entered into legal force on March 7, 2021. From this date, the period for cassation appeal is limited to six months from the date of entry into force of the verdict or other final court decision in a criminal case. For a convicted person who is in custody, this period is calculated from the date of delivery to him of a copy of the sentence (decision) that has entered into legal force.
Thus, at present, the cassation period for appealing a verdict is no longer unlimited. Those who did not have time to appeal a cassation verdict or decision that came into force from 10/01/2019 to 02/24/2021 can do so until 08/24/2021.
Cassation instance
A cassation appeal in a civil case is filed with the cassation authority. The cassation authorities are:
- on appeal rulings; on court orders, decisions and rulings of district courts and magistrates that have entered into legal force - the presidium of the supreme court of the republic, regional, regional court, court of a federal city, court of an autonomous region, court of an autonomous district;
- on appeal rulings of district (naval) military courts; on decisions and rulings of garrison military courts that have entered into legal force - the presidium of the district (naval) military court;
- on decisions and appeal rulings of the presidiums of the supreme courts of republics, regional, regional courts, courts of federal cities, courts of an autonomous region, courts of autonomous districts; against decisions and rulings of district courts that have entered into legal force, adopted by them in the first instance, if these decisions and rulings were appealed to the presidium of the supreme court of the republic, regional, regional court, court of a federal city, court of an autonomous region, court of an autonomous district, respectively - to the Judicial Collegium for Civil Cases of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation;
- on decisions of the presidiums of district (naval) military courts; against appeal rulings of district (naval) military courts, as well as against decisions and rulings of garrison military courts that have entered into legal force, if these court decisions were appealed to the presidium of the district (naval) military court - to the Judicial Collegium for Military Personnel of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation .
Drawing up a cassation appeal
When drawing up a cassation appeal in a civil case, you should adhere to the requirements of Article 378 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation and take the presented sample of a cassation appeal as a basis.
The cassation appeal must contain the following information:
- full name of the cassation court
- procedural status, name and address of the person filing the complaint
- name and procedural status of other persons participating in the civil case, their addresses
- document name - Cassation appeal
- details of all court decisions appealed in cassation
- arguments and grounds for which court decisions are illegal and subject to cancellation
- demands to cancel court decisions
- list of documents attached to the cassation appeal
- date and signature of the person filing the complaint
When appealing court decisions, the cassation instance has the power to cancel or change court decisions in the case or leave them in force. The requirements in a cassation appeal must comply with the powers of the cassation court. The full list is given in Article 390 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation.
Copies of court decisions attached to the complaint must be properly certified. Photocopies of documents are not accepted.
Deadline for filing a cassation appeal
The deadline for filing a cassation appeal in a civil case is 6 months from the date the court decision entered into legal force (Article 376 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation).
The specified period begins for decisions and rulings of the court of first instance from the moment the appeal ruling is issued. For appealing appeal rulings, the period begins from the moment they are adopted. For a court order, the period begins to run from the moment the time for filing objections expires.
The period for cassation appeal is calculated from the next day after the court decision enters into legal force and expires on the corresponding date after 6 months. If the deadline for filing a cassation appeal is missed, it can be restored on the grounds specified in Article 112 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. To do this, a corresponding application is submitted to the court of first instance.
| Note! |
| Application for restoration of the deadline for filing a cassation appeal |
General provisions
Before filing a cassation appeal in a civil case, interested parties should study the norms of Chapter 41 of the Code of Civil Procedure of the Russian Federation. This section contains requirements for drawing up an appeal, rules of jurisdiction, regulates the work procedure of government bodies, etc.
The practice of the courts was summarized in Resolution of the Plenum of the Armed Forces of the Russian Federation dated December 11, 2012 No. 29. This document contains provisions regarding the calculation of the deadlines for filing a cassation appeal, the procedure for their restoration if missed, and other recommendations.
The role of cassation in civil proceedings is to verify compliance with the law. The government agency investigates the case and determines whether the provisions of the regulations were violated. Consideration of the case at this stage does not involve the presentation of new evidence, challenging the order of examination of documents, etc.
A cassation appeal should be filed only in cases where the identified violations had a significant impact on the court’s decision. In each process, the sign of materiality is established separately. The main requirement is to exclude a violation; the dispute will be resolved differently.
A person may not appear as a participant in the process, but the execution of the decision affects his interests. In this situation, a citizen can immediately file a cassation appeal if there are grounds for this.
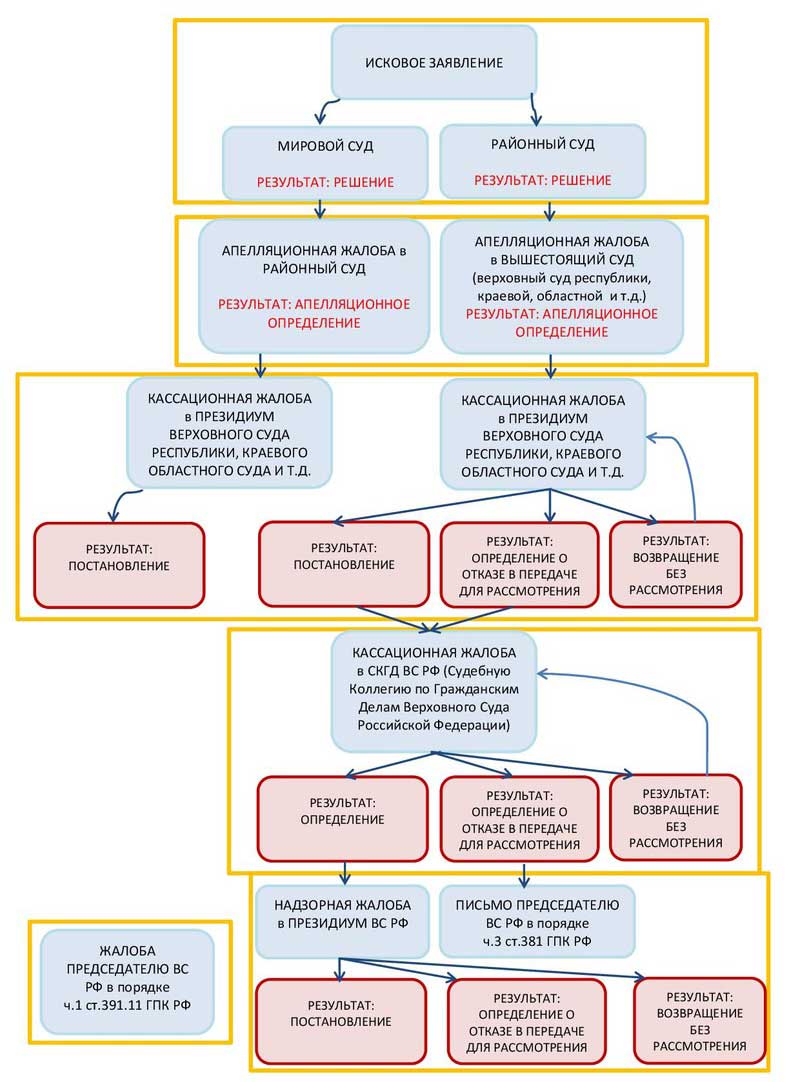
Filing a cassation appeal in a civil case
A cassation appeal is filed directly with the cassation court. This is usually done via postal service. When filing a cassation appeal in violation of the deadline, it is necessary to attach a copy of the court ruling to restore this deadline.
Copies of the appealed court decisions are attached to the complaint. Please note that copies of court decisions attached to the cassation appeal must be properly certified by the court of 1st instance.
How are copies of judicial acts properly certified?
The procedure for certification of a copy is established by the Instructions for Judicial Proceedings.
Copies of judicial acts issued by the court must be certified by the signatures of the judge, the court secretary, as well as the official seal of the court. On the front side of the last sheet, under the text, the stamp “Copy is correct” and the seal of the court are affixed. A “COPY” stamp is placed in the upper right corner of the first sheet of the document.
If a copy of a court order consists of several sheets, then all sheets must be numbered, stitched with a strong thread, the ends of which are brought out on the back side of the last sheet of the copy of the document, or stapled using a stapler; on the reverse side of the last sheet, in the places of fastening, a sticker is placed with the certification inscription “numbered and sealed by ____ sheets, signature ______” indicating the court that is issuing a copy of the document, the signature is sealed with the official seal of the court. The seal is placed in such a way as to partially capture the piece of paper that seals the ends of the thread or the place of fastening.
When filing a cassation appeal, a state fee is paid, except in cases where the applicant has benefits for its payment.
| The current amount of state duty payment, payment benefits as of today: | |
| state fee to court |








