19.07.2019
0
68
5 minutes.
When applying for a job, the employer and the person applying for the vacant position sign an agreement. From this moment on, a labor relationship arises between them. Each party has a strictly regulated list of rights and obligations defined by the basic law in the field of interaction between employees and employers - the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
NMA
The position of women in the world of work is regulated by a number of international Conventions, ratified first by the USSR and then by Russia;
- ILO Convention No. 45 (1935) Concerning the Employment of Women in Underground Work in Mines of Any Kind;
- ILO Convention No. 100 (1951) Concerning equal remuneration for men and women for work of equal value;
- ILO Convention No. 111 (1958) Discrimination (Employment and Occupation) Convention;
- ILO Convention No. 156 (1981, ratified 1997) on Equal Treatment and Opportunities for Men and Women Workers: Workers with Family Responsibilities.
International standards are included in Russian legislation.
So in particular, Art. 3 of the Labor Code prohibits discrimination, i.e. restriction of labor rights and freedoms or receipt of any advantages depending on the gender of the employee. At the same time, it is not discrimination to establish differences, exceptions, preferences, as well as restrict the rights of female workers, which are due to the special concern of the state for persons in need of increased social and legal protection .
Discrimination in labor laws
The word “discrimination” came into use from the Latin language (discriminatio).
The Labor Code of the Russian Federation in Article 3 defines what constitutes discrimination in the field of labor relations. This is the illegal establishment of various kinds of restrictions that lead to the inability of certain categories of citizens to perform labor duties, based on the principle of equality along with others.
ILO Convention No. 111 of June 25, 1958 and the Labor legislation of the Russian Federation regulate a unified procedure for the implementation of labor functions by each person, without infringing on rights due to any peculiarities.
Employers can choose a suitable candidate for a vacant position only by assessing qualities such as education, experience, and professionalism in the relevant field.
It is prohibited to refuse employment only because the employer is not satisfied with:
- the employee's commitment to a particular religion,
- race of a person, skin color, belonging to one sex or another, age data,
- speaking in another language,
- position and status in society,
- place of living,
- family and marital status.
It must be remembered that if at an interview or in an advertisement for a vacant position the employer indicates that he requires employees who do not have anything from the above list, or, conversely, is recruiting people of the same gender or race, then this is regarded as discrimination in the field labor.
If an employer cuts wages or bonus payments, for example, only because a person often has to be on sick leave or because he refuses to attend corporate events, then in this case we can talk about the infringement of the rights and interests of the employee.
The employee can only be required to have appropriate professional training, experience, and education. For example, teachers, drivers, as well as workers employed in underground production in accordance with the law, are subject to special requirements (see articles 328, 330.2, 331).
Thus, the fact that an employer requires certain qualities from a citizen due to the specifics of the profession will not constitute discrimination.
Law of April 19, 1991 No. 1032-1-FZ “On Employment in the Russian Federation” also states that when posting job advertisements, it is prohibited to present requirements to citizens regarding a specific race, nationality, origin or gender, age, language and other criteria that cannot influence the level of professionalism of a person in the required field (clause 6 of Article 25).
Criteria that establish advantages for some employees without regard to their business qualities are discriminatory.
For your information! The greatest disadvantage from employers is faced by applicants or employees who have HIV.
At the legislative level, there is also a prohibition against refusing to hire such citizens or dismissal in connection with the specified diagnosis (Law No. 38-FZ dated March 30, 1995 On preventing the spread in the Russian Federation of the disease caused by the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV infection)).
Hard labour
When hiring women, the employer is obliged to comply with the standards established by Art. 253 of the Labor Code, according to which the use of women’s labor in heavy work and work with harmful and (or) dangerous working conditions, as well as in underground work is limited.
Currently, there is a List of heavy work and work with harmful or dangerous working conditions, during which the use of women’s labor is prohibited, approved by Government Resolution No. 162 of February 25, 2000.
If, in violation of the requirements of labor legislation, a woman was allowed to perform such work, then the employment contract with her is terminated on the basis of Article 84 of the Labor Code if it is not possible to transfer her to another job available to the employer that she can perform. In this case, the woman is paid severance pay in the amount of average monthly earnings.
It is prohibited to employ women in jobs involving lifting and manually moving heavy loads that exceed the maximum permissible standards for them. These standards were approved by Resolution of the Council of Ministers - Government of the Russian Federation dated 02/06/1993 No. 105.
| Nature of work | Maximum permissible load weight |
| Lifting and moving heavy objects when alternating with other work (up to two times per hour) | 10 kg |
| Lifting and moving heavy objects continuously throughout the work shift | 7 kg |
Contacting the Labor Inspectorate

The Federal Service for Labor and Employment is a body that is empowered to monitor the rights and interests of workers in the performance of their labor duties. The State Tax Inspectorate can also be notified in the event that an employer publishes a discriminatory job advertisement.
Please note! This service does not solve a person’s problems in the workplace, but it disciplines the employer, holding him accountable for violations committed in the field of labor legislation.
How can a citizen contact the State Tax Inspectorate:
- in person, appearing at the territorial authority,
- by mail,
- by sending an appeal electronically on the website onlineinspection.rf/problems.
Algorithm of actions for a citizen when sending a complaint to the State Tax Inspectorate:
- find out which department of the service controls the relevant organization (if the region of residence is small, then there is only one territorial body of the State Tax Inspectorate),
- write a complaint indicating the reason and justification for the violation,
- collect evidence in the form of documents, attach copies to the complaint,
- Submit the application and attached documentation to the State Tax Inspectorate in a convenient way.
Fines of the Labor Inspectorate for legal entities in 2019.
complaints against the employer to the labor inspectorate for free in word format
How to compose the appeal itself and write an application?
There is no uniform standard for the complaint form, however, in order to receive a response from the authorized body, the following information must be indicated in the application:
- details of the body and name of the head to which the complaint is filed,
- personal data of the applicant and address of residence (registration), telephone,
- information about the employer: details of the legal entity or individual entrepreneur, location address, contact details,
- essence of the appeal: date of violation by the employer against the employee, reasons and justifications, reference to the rules of law, option for resolving the controversial situation,
- date of filing the complaint, signature, transcript.
The period established by law for sending a response to citizens' appeals is one month. If violations are detected on the part of the employer, the State Tax Inspectorate has the right to contact the Prosecutor's Office. The citizen is also not deprived of the opportunity to take measures in this direction.
Translation
In accordance with Art. 254 of the Labor Code for pregnant women, in accordance with a medical report and at their request, production standards, service standards are reduced, or these women are transferred to another job that excludes the impact of adverse production factors, while maintaining the average earnings for their previous job.
Requirements for working conditions for women during pregnancy are enshrined in Section 4 of SanPiN 2.2.0.555-96 “Hygienic requirements for working conditions for women,” approved by Resolution of the State Committee for Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision of Russia dated October 28, 1996 No. 32.
Until a pregnant woman is provided with another job that excludes exposure to adverse production factors, she is subject to release from work with the preservation of average earnings for all working days missed as a result at the expense of the employer.
A similar guarantee also applies to women with children under the age of one and a half years. In accordance with Part 4 of Art. 254 of the Labor Code, such women, if it is impossible to perform their previous job, are transferred at their request to another job with wages for the work performed, but not lower than the average earnings for the previous job until the child reaches the age of one and a half years.
True, in this situation, the employer has no obligation, if it is impossible to transfer the woman to another job, to release her from work while maintaining her average earnings. In return, the employee is given the right to take parental leave.
Labor Code of the Russian Federation Article 21. Basic rights and obligations of the employee
The rights and labor responsibilities of a working person are enshrined in Article 21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. When signing an agreement, employers and applicants must be aware of and comply with mutual written agreements. The person who works receives a salary, and the manager pays it on time and in full, including all compensation payments. The right of one party is the duty of the other. The legislative norm regulating the actions of the employee is Art. 21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Basic rights of an employee
An employer cannot require a person to perform functions that are not specified in the main document. The administration is responsible for illegal actions. The rights of an employee under the labor code are listed in Art. 21 Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- sign, change and supplement, as well as terminate the employment contract, observing the rules specified in regulations;
- apply for the activities set out in the contract;
- receive a salary for the activities specified in his contract;
- have a place equipped in accordance with regulatory labor protection requirements;
- have equal pay for equal work without any discrimination;
- rest during paid leave on an annual basis, take days without pay;
- demand that the organization’s managers fulfill the terms of contracts;
- protect your rights by all legal means;
- appeal against the actions of the organization’s employees in the field of labor and other relations directly connected with them;
- receive compensation for material damage caused to health if it was received during the performance of work duties;
- refuse to perform work activities if facts arise that pose a threat to his physical health;
- receive information in areas related to the labor function specified in the contract, including full access to reliable information about the state of labor conditions and safety;
- arrange life and health insurance for subordinates on the part of the employer;
- keep confidential personal data stored by the employer.
Main responsibilities of the employee
Let us list what responsibilities the Labor Code of the Russian Federation defines for employees. A person must fulfill the following requirements:
- conduct activities in accordance with the work schedule;
- be disciplined in accordance with agreements, labor, collective agreements, acts of the organization;
- comply with labor protection standards and legislative norms;
- preserve company materials and equipment;
- notify the employer of life-threatening situations;
- not to disclose trade secrets;
- compensate the organization for damage if it was caused during the performance of work duties.
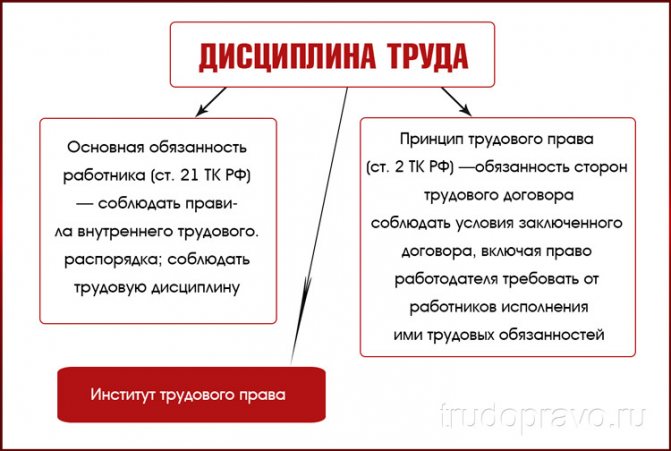
It is important to know! The obligations of an employee under the labor code are the object of close attention from the employer. Failure to comply will result in disciplinary action.
Working conditions
The Labor Code prohibits involving pregnant women in overtime work, night work, weekends and non-working holidays.
It is illegal to employ pregnant women in such work, even if it is done with their written consent or even at their request.
In addition, the employer also does not have the right to send pregnant women on business trips, and pregnant women and women with children under 3 years of age cannot be involved in work performed on a rotational basis.
Women with children under 3 years of age can be sent on business trips, involved in overtime work, night work, weekends and non-working holidays, only with their written consent , and provided that this is not prohibited to them in accordance with a medical certificate.
This guarantee also applies to the following categories of employees:
- workers with disabled children;
- workers caring for sick members of their families in accordance with a medical report;
- mothers and fathers raising children without a spouse under the age of 5 years.
Application to the Prosecutor's Office
The prosecutor's office is a state law enforcement agency that exercises control and supervision in the application of laws, including those related to labor relations.
complaints to the prosecutor's office against an employer for free in word format
The appeal must contain the following information:
- details of the government agency,
- personal data of the applicant,
- the name of the document is “complaint”,
- information about the violator - legal entity or individual entrepreneur,
- essence of the appeal, description and arguments, references to legal norms,
- proposals to correct the controversial situation and resolve the conflict, on measures to bring to justice,
- an attachment in the form of documentation confirming the above in the complaint,
- date and signature.
When requesting labor documents from an employer, the latter must comply with the request within three days. The best option would be to provide the Prosecutor's Office with as much evidence as possible of the violation of the employee's rights.
If a group of workers suffers from the arbitrariness of the employer, then a collective complaint is filed.
Know! After the inspection, the Prosecutor's Office has the right to issue an order to a legal entity or individual entrepreneur to eliminate violations in the field of labor legislation.
How can I contact the Prosecutor's Office with a complaint?
- in person, by appearing at the territorial department of the Prosecutor's Office in the relevant constituent entity of the Russian Federation. You must have a passport, application and documentary evidence with you, which are handed over to an authorized employee under a personal signature on both sides,
- through the services of a representative who is authorized to perform certain actions in accordance with a notarized power of attorney. In addition, he must provide a passport for identification,
- by sending a complaint by mail. The best option is to send registered mail with return receipt requested. The applicant will have in his hands a document confirming that the government agency has received the submitted complaint and a package of documents.
The period for consideration is 30 days - this is established at the legislative level.
It should be noted that in some cases the Prosecutor's Office only gives general recommendations to the employee or advises to apply for protection of rights to the State Tax Inspectorate or the judicial authorities.
Complain to the Moscow City Prosecutor's Office online.
Part-time work
At the request of a pregnant woman, one of the parents (guardian, trustee) with a child under the age of 14 years (a disabled child under the age of 18), in accordance with Part 2 of Art. 93 of the Labor Code, the employer is obliged to establish part-time working hours . In this case, wages are paid in proportion to the time worked.
in rural areas, in the Far North and similar areas have a special working time regime In this case, wages are paid in the same amount as for a full working week.
If the employer has not established a reduced working time for the specified category of employees, the work they perform in excess of the established working time is subject to payment according to the rules provided for payment of overtime work.
Prohibition of discrimination
Labor legislation establishes a ban on infringement of the rights of workers (Article 2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
This is expressed in the following directions:
- a person cannot be forced to perform labor duties, guided by a threat to the life or health of the employee, his family, or promises to deprive him of material benefits due to the fact that he has distinctive characteristics related to gender, race, origin, nationality, language, religious adherence, etc. .,
- eradication of discrimination in the field of labor relations,
- promotion up the career ladder in accordance with the principle of equality, where the main criteria for assessing the qualities of an employee are education, experience, professionalism, qualification degree.
What to do if your boss finds fault with little things?
Holiday according to BiR
In accordance with Art.
255 of the Labor Code, women, upon their application and on the basis of a certificate of incapacity for work, are granted maternity leave for a duration of 70 (in the case of multiple pregnancies - 84) calendar days before childbirth and 70 (in the case of complicated childbirth - 86, for the birth of two or more children - 110 ) calendar days after childbirth with payment of benefits. The legislation does not provide the opportunity for a woman, while on maternity leave, to continue working and at the same time receive maternity benefits. Thus, a woman needs to choose between maternity benefits and wages.
Holiday to care for the child
According to Art. 256 of the Labor Code, a woman is granted leave to care for a child until he reaches the age of 3 years. Conventionally, this leave can be divided into two periods: parental leave until the child reaches the age of one and a half years, during which the woman receives child care benefits, and child care leave from one and a half to three years. This division is significant only for the purposes of payment of benefits , but from the point of view of labor relations, this is one leave, and the legal status of the woman is the same in both cases.
Parental leave can be used by a woman in full or in parts. A woman can work part-time or at home while maintaining the right to receive state social insurance benefits.
Moreover, the employer does not have the right to refuse a woman to establish part-time working hours.
Breaks
Working women with children under the age of one and a half years are provided, in addition to breaks for rest and food, with additional breaks for feeding the child at least every 3 hours of continuous work, lasting at least 30 minutes each.
At the request of the woman, breaks for feeding the child are added to the lunch break or, in aggregate form, are transferred to both the beginning and the end of the working day with a corresponding reduction.
At the same time, a decrease in the hours actually worked by the employee does not affect the amount of earnings.
Vacations
Annual paid leave, regardless of length of service with a given employer, is granted upon application by a woman before or immediately after maternity leave, or at the end of maternity leave.
Also, a guarantee for the use of annual paid leave at a time convenient for the employee is established for one of the parents raising a disabled child under the age of eighteen.
An employee who has two or more children under the age of 14, an employee who has a disabled child under the age of 18, a single mother raising a child under the age of 14, a father raising a child under the age of 14 without a mother, may be subject to a collective agreement annual additional leaves without pay at a time convenient for them, lasting up to 14 calendar days.
Extra weekend
By virtue of Article 262 of the Labor Code, one of the parents, upon his written application, is granted 4 additional paid days off per month to care for disabled children.
Payment for each additional day off for caring for disabled children is made in the amount of average earnings.
It is not a disciplinary offense for an employee to use additional days off if the employer, in violation of the statutory obligation, refused to provide such days.
Trial
Appeal to the judicial authorities for the protection of violated interests is one of the most popular methods in the field of labor relations. Article 3 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation gives a person the opportunity to file an application in court if an employer diminishes his rights.
In this case, you can demand compensation for material and moral damage. Applications are considered by district courts at the location of the defendant - legal entity or individual entrepreneur.
The period for filing a claim for restoration of rights in the world of work is three months. Upon dismissal - one month from the date of signing the corresponding order or issuing a work book (Article 392 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
claim for the protection of labor rights against discrimination by the employer free in word format
What demands can be made in the pleading part of the statement of claim:
- on recognizing as illegal the employer’s actions to infringe upon the rights of an employee,
- on declaring any action illegal and, at the same time, recognizing it as infringing on the rights of a citizen in the sphere of labor (for example, illegal dismissal and at the same time discrimination due to the fact that a person was fired due to belonging to a certain nationality),
- on recognition of the employer’s actions as fully discriminatory,
- along with other claims for compensation for material compensation and moral damage,
- on the payment of wages and other earnings due to the employee.
It should be noted that the amount of compensation is specified by the employee in the statement of claim, but the final decision regarding the amount of payments is made by the court.
Employees turn to the courts if other protective measures do not work to restore the rights and interests of citizens who have been discriminated against by their employer.
Attention! Our qualified lawyers will assist you free of charge and around the clock on any issues. Find out more here.
Dismissal
Termination of an employment contract at the initiative of the employer with pregnant women is not allowed, except in cases of liquidation of the organization.
A special procedure for terminating an employment relationship during the employee’s pregnancy is also provided for the situation of expiration of the employment contract. In this case, the employer is obliged, upon the written application of the pregnant woman and upon her provision of a medical certificate confirming the state of pregnancy, to extend the term of the employment contract until the end of the pregnancy, and if she is granted maternity leave in the prescribed manner - until the end of such leave.
It is permissible to dismiss a woman due to the expiration of the employment contract during her pregnancy, if the employment contract was concluded for the duration of the duties of the absent employee and it is impossible, with the written consent of the woman, to transfer her to another job available to the employer before the end of her pregnancy.
Increased protection against dismissal is also provided to the following categories of persons:
- women with children under 3 years of age;
- single mothers raising a disabled child under the age of 18 or a young child - a child under the age of 14;
- other persons raising these children without a mother;
- a parent who is the sole breadwinner of a disabled child under the age of 18 or the sole breadwinner of a child under the age of 3 in a family raising three or more young children, if the other parent is not in an employment relationship.
According to Part 4 of Art. 261 of the Labor Code, termination of an employment contract with the employees listed above at the initiative of the employer is not allowed, with the exception of dismissal on the following grounds:
- liquidation of the organization;
- repeated failure by an employee to perform labor duties without good reason, if he has a disciplinary sanction;
- a single gross violation of labor duties by an employee;
- commission of guilty actions by an employee directly servicing monetary or commodity assets, if these actions give rise to a loss of confidence in him on the part of the employer;
- the commission by an employee performing educational functions of an immoral offense incompatible with the continuation of this work;
- a single gross violation by the head of the organization (branch, representative office) or his deputies of their labor duties;
- the employee submits false documents to the employer when concluding an employment contract.
Violations of the labor code by the employer
Basic:
- Failure to comply with the rules when concluding or terminating an employment contract
, as well as unauthorized changes in its subject and conditions; - Incorrect calculation of wages
, as well as
refusal to pay them
, including in the event of dismissal of an employee; - Incorrect organization of labor protection
; - Violations of work and rest regime
; - Refusal to provide guarantees and compensation
; - Failure to comply with disciplinary labor standards
and incorrect use of penalties; - Failure to provide mandatory guarantees
to certain categories of workers provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation; - If you are denied the opportunity to improve your qualifications
; - Violations in the process of adopting regulations
of local significance; - Failure to comply with migration legislation
and hiring foreign labor.