Decoding the meaning of numbers on product barcodes is of interest not only to sellers, but also to buyers. These are noticeable stripes applied in a specific sequence and are of significant importance for identifying the product. They are used to determine data, display the type in warehouse and trade accounting, and separate different tastes or colors within one item during inventory. There are different coding systems, functions and application specifications.
Barcode on packaging: what is it and what is it called
This designates a picture that is attached or printed to automate accounting. It helps to identify a thing, identify a specific variety and check information about it in a common database. With its help, you can reduce the time for data processing and optimization of warehouse space.
It looks like the code contains everything about the product, but in reality it's just 2D graphics that are meant to be read. All information will be stored in the memory of the server of the enterprise that produces shoes, clothing and many other products.
You can find different types of barcode:
- with a unique product number;
- with detailed information about the manufacturer;
- to optimize everything that is packaged in different containers - packs, pallets.
EAN code readers
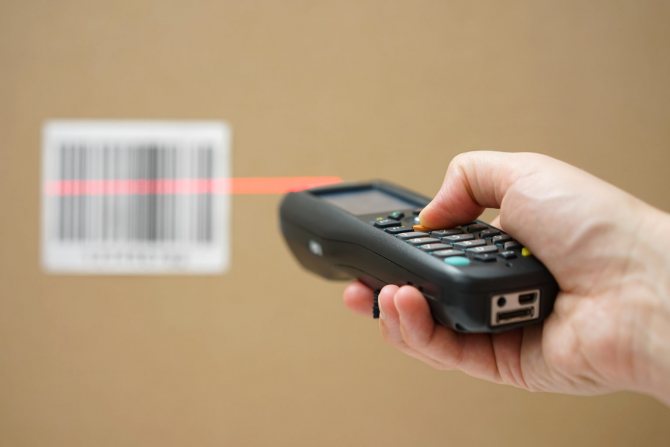
To read information from hatching use:
- cash scanning devices;
- optical readers in the form of a laser gun, pen, pencil, etc.;
- portable and stationary mechanisms that allow you to read the code at a distance of 0.6-6 meters.
The simplest of the devices presented is a pencil. By running it through the code, the cashier-operator enters information about the product into the cash register computer upon purchase. However, this contact reading is only suitable for small shops.
Large markets use D-500 format scanners that recognize codes at a distance and in different orientations of the label or packaging using multi-beam scanning. The decoder built into them is capable of “unraveling” the encoding of all known standards.
After receiving information about the purchased product, the reading mechanism transmits the read data to the central warehouse system, which subtracts these products from those available. When there is a critical balance of goods, the system sends a signal about the need to replenish it.

Almost all readers are able to recognize fake shading. But in order to recognize barcodes of countries around the world, they need the following conditions: the location of the code is no closer than 2 cm from the edge of the package or label, in the lower right corner, without any text or image applied to it.
Business Solutions
- shops clothing, shoes, groceries, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
History of invention
Back in 1948, many industries faced the serious problem of needing reading to optimize warehouses and speed up order processing. Bernard Silver, a graduate student at the university, took up the issue of labeling with friends. The beginning of the experiments was not the most successful - ultraviolet ink was used, which quickly lost color and was expensive.
The right decision came suddenly - on the beach. The first code we needed looked like an elongated Morse code - it was wide and narrow stripes. To read them, they set up technology that was usually used to record sound for films.
In 1949, the invention was sent for a patent. And in 1951 it was rejected because it was considered too expensive to implement and use. In 1952, the uniqueness of the created system was documented, but due to lack of finances and lack of sponsors, the idea was sold to RCA.
In 1974, the first supermarket appeared in which products were sold via swipe. Now the receipt from this purchase is kept in the American History Museum as a symbol of the beginning of a new era.
Barcode history
Barcodes of countries of origin of goods originate in the late forties of the 20th century, when students Bernard Silver and Norman Woodland tried out their new invention. They received a patent for this means of automatic information processing in 1952.
Refuting the legend that the very first product to have a barcode applied was Wrigley (chewing gum), I would like to clarify that this was only the first product from which the scanner read information from the barcode. The item was randomly selected by the cashier while testing the new system.
In 1981, the United States Department of Defense decided to use the CODE39 barcode format to label all military goods. This became the trigger for the massive use of barcoding around the world. The system was so well thought out that the used barcodes of the countries producing goods are not outdated to this day.
The principle of a bar code on any product
This is the name for creating successive black and white stripes with different widths. This is an encoding that, at the moment of reading, transmits data through scanning and decoding technology.
This kind of work is considered one of the most common methods of identification.
The most famous are JEAN-13 and EAN-8. They all have certain meanings. What does a barcode consist of:
- The initial 2-3 characters indicate the country where the information bank is located. The numbers are distributed by a special international organization.
- The next 4 are the manufacturer's numbers. It is assigned by the national authority of the country of origin.
- Another 5 are data about the product being sold. Here, the company manufacturing the product can independently register and assign registration numbers within production. Among these numbers, important distinctive signs for storage and sale are usually encoded - color, weight, dimensions, variety, taste.
- The last character is the check number. It is required to complete reading using the scanner. Find it by performing simple arithmetic operations.
The nominal size of the entire encoded message is 31.35 mm, but nothing should be placed on either side of it, so the full size with margins is 37.29 mm. The first and last characters will be elongated to highlight the start and end of the scan.
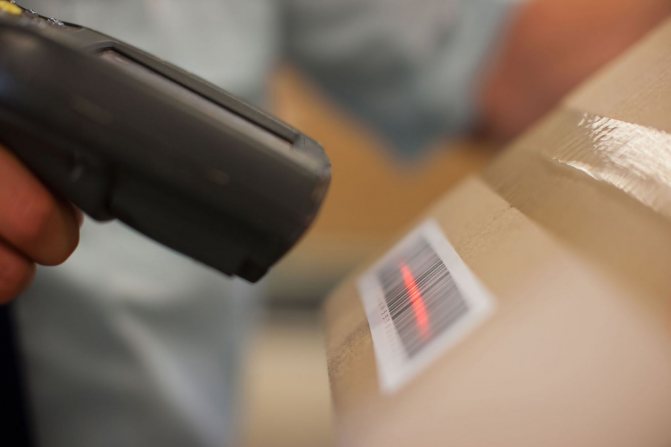

Checking the barcode of cosmetics, goods
The authenticity of the barcode is checked by the last, thirteenth digit. To do this, each code character is assigned a serial number from 1 to 12. Then:
- Add all even numbers and multiply them by 3.
- Sum up all odd numbers.
- The “odd” amount is added to the “even” amount.
- Only the last character is left from the resulting value (if it was equal to 324, then 4, if 23, then 3, etc.)
- This single number is subtracted from ten - the difference must be equal to the check digit.
To check the authenticity of the barcodes of the countries where goods are produced, this simple calculation is enough.
Functional
A barcode has more useful functions than many other signs that carry information. It will be useful in any enterprise, store, warehouse.
Additional features:
- Automated identification of varieties using reading devices.
- Automation of product accounting in warehouses.
- Control of movements, location of any element of the party, their quantity.
- Ease of management of loading, transportation, shipment, localization indoors.
- The speed of loading and order collection increases significantly, and the risk of errors is minimized.
- Building an improved customer service culture.
- Marketing research can be carried out faster, and its results will be more reliable and accurate.
How to find out a product by barcode online
There are many online services for checking goods by barcode. Let's test them, to check we'll take this sausage from Pyaterochka:

Progaonline
The form for entering the code is located here: https://progaonline.com/kod. We enter our code, we receive information: red sausage from Russia, 300 grams, barcode - authentic. Here, by the way, you can check up to 30 products at the same time.
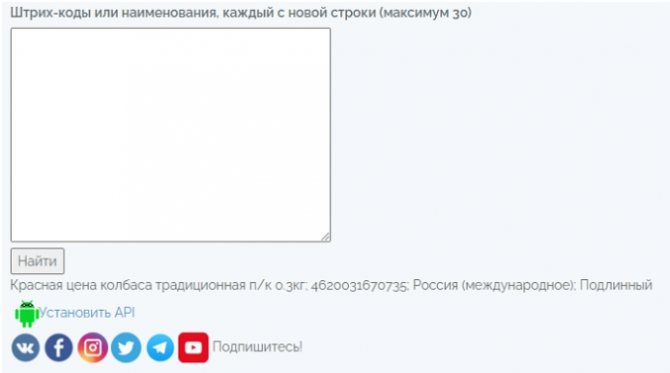
Barcodesdatabase
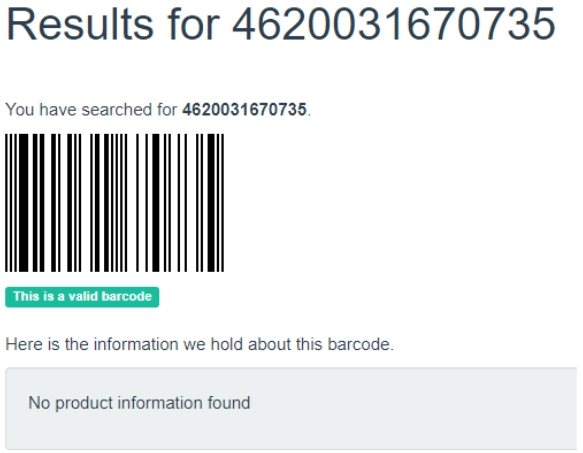
Link to the page we need: https://barcodesdatabase.org/barcode-search/. We enter our code - no result, although the site says that the code has a right to exist - the verification number is correct.
Considering that this database is intended primarily for goods from the EU and the USA, it is not surprising that nothing was found in the database.
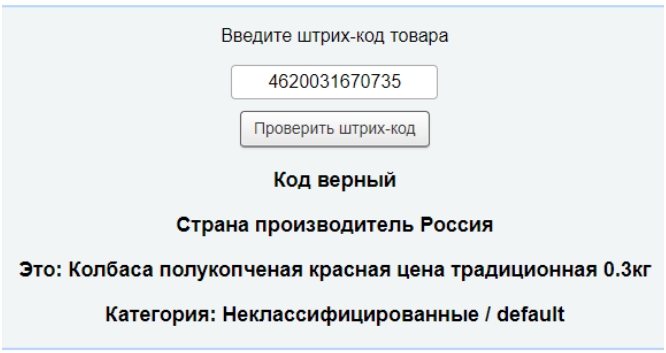
Service-online
Another Russian-language service for online checking of goods. Link to the verification page: https://service-online.su/text/shtrih-kod/. Enter 4620031670735, click “Check” - we get the information:
We can conclude that it is better to search for goods from the CIS in Russian-language databases, and for goods from other countries in English-language databases.
Types of barcodes and their examples
There are 3 forms:
- EAN-13. Full address of 13 characters, only numbers are used.
- EAN-8. Short type, includes 8 storage media.
- EAN-128. Enlarged, this option can contain any number of characters, numeric and alphabetic, they are combined into different groups.
If you need to understand what a barcode looks like, we have provided an example. The first two varieties from the list cannot have any other designations, only numbers. For detailed types, any number of letters, brackets, and other characters can be placed.
EAN-8 encoding is usually used for small batches or small-sized products. The reason for using such designations is to test products on a fast assembly line. The shorter the length of the strips, the faster they will be read without the risk of getting erroneous results.
The extended format is usually used to provide data to another enterprise to which the part or consumable is sent. A barcode icon can contain a large number of numbers. The digital type is so named not because of its maximum length, but because of the Code-128 dictionary that is used to compile the list. It can mean anything, usually contains encoded:
- Name;
- best before date;
- date of manufacture;
- size;
- volume;
- individually assigned manufacturer number;
- number of batch or shift;
- variety.
The main one remains EAN-13, which is constantly used in light industry.
How is information on a barcode about the manufacturer of a product deciphered?
This data is issued by the international company EAN to each enterprise separately. Using this order, the possibility of two different elements with the same number appearing simultaneously is eliminated.
There are 2 coding methods - linear and two-dimensional. The first view is read only horizontally. This way you can encode a small volume, only 20-30 characters. Even an inexpensive simple scanner can read such numbers.
The second type is called two-dimensional. To count it, you will need a special scan. With its help, you can encrypt an increased amount of data and release it by simply reading it. It is deciphered in two directions - vertical and horizontal. Among the popular ones:
- Aztec;
- Datamatrix;
- Data Glyph.
What does a barcode on a product mean? It encodes the most important information about the product or service being sold. More often they apply the American unified mark in the abbreviation UPC, created according to the recommendations of the European association.
Independent decoding by numbers
Enter 13 digit barcode:

You can check the barcode by performing arithmetic calculations. Let's look at the example 4213714512516.
We carry out calculations:
- We sum up the numbers in even places and multiply the resulting sum by 3: (2+3+1+5+2+1) × 3=42.
- Now we add the numbers in odd positions: 4+1+7+4+1+5=22.
- We find the checksum of the values obtained in the two previous paragraphs: 42+22=64.
- Select the last digit - 4.
- Subtract 4 from 10: 10-4=6.
- We compare the last value with the control: 6=6.
Compliance with the calculated value indicates the correctness of the barcode, but is not 100% proof of the originality of the product. However, the discrepancy detected as a result of the calculation indicates that the product being tested is a fake.
Business Solutions
- the shops
clothes, shoes, products, toys, cosmetics, appliances Read more
- warehouses
material, in-production, sales and transport organizations Read more
- marking
tobacco, shoes, consumer goods, medicines Read more
- production
meat, procurement, machining, assembly and installation Read more
- rfid
radio frequency identification of inventory items More details
- egais
automation of accounting operations with alcoholic beverages Read more
Details about the EAN-13 variety
This is an image consisting of a unique international number. Under the stripes it is duplicated in Arabic numerals. There will be 13 of them in this variety.
This order is necessary to make visual reading possible in case of physical damage to the code. If the picture is blurry, scratched, or cannot be read by the scanner for other reasons, simply enter the number below it into the database.
There is an idea that if you decipher this message, you can see a lot of important information about the item being sold. In fact, everything is different: this indicator contains an encrypted message that will be the key to the database.
Coding is a voluntary matter, so the manufacturer has the right to receive his number in any department. Then it is assigned the code of the country in which the documents were received. Let's look at what will be encoded in the product block. This is a total of 5 digits; if we move from left to right, we get the following data:
- Name;
- properties important to buyers;
- weight, dimensions;
- ingredients included;
- color
If you look at the barcode vertically, the last mark is the control mark. This is not a random number, but calculated from the sum of those in front. It is calculated according to the algorithm:
- everything in even positions is summed up;
- then the result must be multiplied by 3;
- odd numbers are added to each other;
- the total from sections 2 and 3 is added up;
- the nearest multiple of 10 to the amount obtained in step 4 is revealed;
- the difference between 5 and 4 is calculated.
What happens will be the final one in the code. This serves to control the reality of the products on sale. The “>” icon completes the picture. It shows that the goods were manufactured in accordance with the license.
Manufacturer country code
The country of manufacture code has two or three characters, and the company code has four or five characters. Products that are large in size may have a short code consisting of eight digits - EAN-8. #13 #13As a rule, the country code is assigned by the International Association EAN. We draw the attention of consumers to the fact that the strange code never consists of one digit .
Sometimes the code printed on the label does not correspond to the country of origin stated on the packaging; there may be several reasons.
- First: the company was registered and received a code not in its own country, but in the one where the main export of its products is directed.
- Second: the product was manufactured at a subsidiary.
- Third: perhaps the product was manufactured in one country, but under a license from a company from another country.
- The fourth is when several companies from different countries become the founders of an enterprise.
Correspondence table of country barcodes in the EAN system.
How a unique ITF-14 barcode is generated
It is used to establish warehouse accounting and speed up the collection of orders or components. It is attached to a container - individual or intended for a group of things.
If we consider such a sequence as a scanner, then the TSD or database will display not only the type of product, but also the quantity contained in the pack.
This encoding differs from EAN-13 in the appearance of the first additional digit with the type of kit. The last number is also considered a control number, but is calculated without taking into account the add-in.
This code is applied to the packaging in the form of a sticker, drawing or using a stencil. This is a larger image, but is intended to be attached to the packaging rather than the item.
Features of use:
- If the item does not exceed 40*30*20 cm in size, then it is enough to stick it on one area.
- If the dimensions are larger, then the code is applied on three sides for easy verification.
What tools exist to decipher a product barcode (and “encryption”)
Algorithms for decoding one-dimensional and two-dimensional barcodes, as a rule, are included by default in most modern means of recognizing them - that is, scanners used in a particular industry. First of all - cash register, warehouse, industrial scanners.
Various mobile applications for decoding barcodes are publicly available - for example, Barcode Scanner (LINK).
QR barcode scanner (LINK).
In many cases, mobile applications can thus not only decipher code in terms of computing "understandable" data - but also present "actually understandable" data to the user.
There are many sites where you can decipher a particular code by downloading its image as a graphic file (for example, this site is LINK).
True, the functionality of such sites in many cases is limited to providing only “understandable” data. But the user can find “really understandable” ones if he wishes.
For example, if he has at his disposal the EAN-13 code for a product manufactured in Russia, then he can, by entering this code on a special page on the website of the Russian representative office of GS1, download key information about the product using it - LINK.

In turn, “encryption” of the code can be done in different ways, depending on the specific standard and purpose of the code. If you need to generate a unique (and legal) EAN-13 product code, then you need to contact GS1: this organization will assign manufacturer and product identifiers defined by the standard.
If you need to generate a QR code based on text data, you can use any of the publicly available online services (for example, THIS).
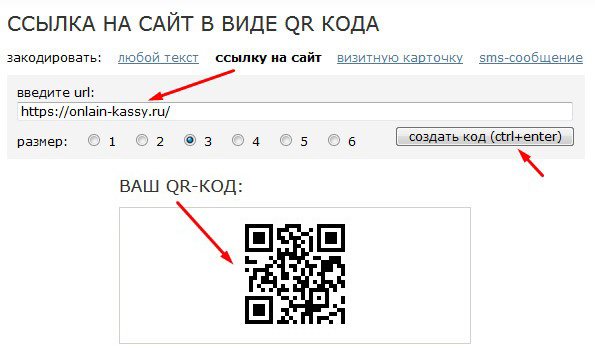
There are many services for one-dimensional codes with free selection of encrypted data (for example, THIS).
They can be used if, as an option, it is necessary to encrypt the weight code using the EAN-13 standard, or assign a code to the cargo according to the GS1-128 standard.
Table of numbers indicating countries of the world
| Belarus | 481 |
| China | 690 |
| RF | From 460 to 469 |
| Great Britain | 50 |
| Slovenia | 383 |
| Croatia | 385 |
| Spain | 84 |
| Germany | From 400 to 440 |
| Portugal | 560 |
| South Africa | From 600 to 601 |
| Tunisia | 619 |
| Taiwan | 471 |
| Uzbekistan | 478 |
| Cuba | 850 |
| France | 30-37 |
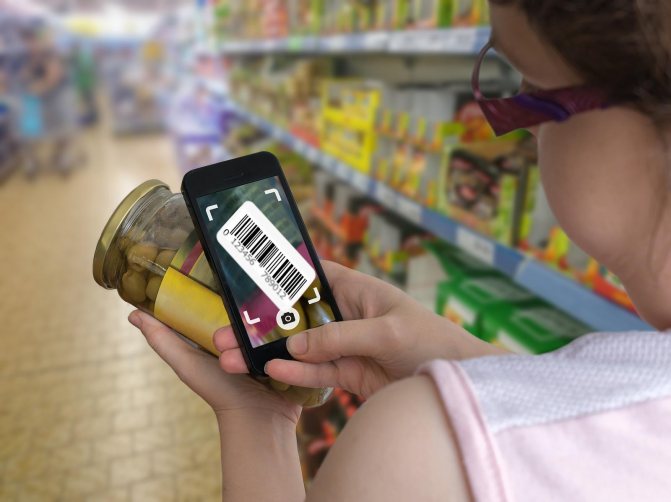

How to decipher information in a barcode without numbers
For all products, the company must create a separate unique code. Sometimes the number under the black and white stripes is unreadable, but even then you can figure it out. This should be done by a special scanner, but if absolutely necessary, it can be examined manually.
The encoding involves dividing the entire pattern into 3 sections, with longer stripes serving as the boundaries. This is noticeable without special equipment - a couple of long lines at the beginning, the same number in the middle and at the end. They are needed to facilitate the reading process for both technology and humans.
Each module has its own width, it can be in one of 4 types. The thinnest of them will be 0.33 mm. To measure, you may need a magnifying glass and a special ruler.
The thickness is then recorded on the left side between the elongated identifiers. How many numbers are used in a barcode? Each number is encrypted with four characters.
When all combinations from medium to long have been entered, the same counting begins from the right side to the center. Then everything is translated into real marks:
- 3211=0;
- 2221=1;
- 2122=2;
- 1411=3;
- 1132=4;
- 1231=5;
- 1114=6;
- 1312=7;
- 1213=8;
- 3112=9.
This technically complex path can be taken to obtain a simple digital code for the database. But usually it is enough to consider everything as a scanner or enter the name into the search engine of the store’s repository.
To purchase all the equipment for the operational operation of the enterprise, you should contact Cleverence. The company's employees understand the types of scanning and printing devices and will help you determine the tasks of your business and select the appropriate equipment and software for them.
What is “encrypted” in two-dimensional codes
A two-dimensional barcode is indeed more technologically advanced compared to a linear one. It contains not stripes and spaces (not only them), but other, more complex shaped elements - squares, dots, lines and others. There are incomparably more options for their relative arrangement compared to the options for the relative arrangement of “spaces and stripes,” and therefore a much larger volume of data can be encrypted into one two-dimensional barcode compared to a one-dimensional code.
As with traditional codes, the order in which the “squares, dots and lines” are relative to one another—and the order in which “human-readable” data (as well as “actually understandable data”) corresponds to them (their combinations) is determined by a specific barcoding standard.
A distinctive feature of two-dimensional barcodes is that they initially encrypt mainly “really useful data” - that is, information that is ready for perception. In many cases, there is no intermediate stage in which the “useful data” - obtained directly from the code - is compared with the information in the database, which is provided for by the standard. But the search for such a match can certainly be done on a regular basis.
“Single-step” decoding of a two-dimensional barcode is possible precisely because of its large capacity: there is no need, unlike a linear code, to place part of the data on a third-party source. At the same time, appropriate decryption usually requires significant computing power. Previously, this was achieved by embedding expensive high-performance microcircuits into barcode scanners. Now even the cheapest mobile gadgets show similar performance. The scanners themselves, equipped with the necessary hardware components, have also become cheaper. Actually, this is the reason for the fact that two-dimensional barcodes are a relatively new phenomenon for the mass market.
The following popular two-dimensional barcoding standards can be distinguished:
- QR code .
Easily recognized by the presence of 3 squares located on the upper right, right and lower left corners. It was originally created for automobile manufacturers from Japan. But later it began to be used everywhere, including in retail trade. Can encrypt almost any data - text, numeric. Theoretically, even the simplest executable commands and small graphic images.
In practice, the code is used to track the movement of goods, identify individual objects, their processing time, and ensure communication between the supplier and the consumer. It is popular to use a QR code as a business card in business.
A QR code can store data up to several kilobytes. The optimal placement is 2-3 KB - so that the algorithms for protecting information from reading errors, which are provided for by the standard, function (using them, you can ensure that the code is read if up to 30% of the information is damaged). Thanks to this option, QR codes can be modified in various ways - for example, by adding drawings to some of its sections (as an option, brand logos). This will make the code stand out from the rest, and at the same time preserve the ability to read information from it (of course, if the remaining areas outside the picture are not damaged).
If necessary, you can use a special type of identifier - Micro QR. It allows you to encrypt up to 35 numbers and up to 21 letters in a minimum area. In many cases, it is significantly less than what would be occupied by a one-dimensional barcode in which similar data is encrypted.
- DataMatrix.
This code is notable because it was the one that the Russian legislator chose as an identifier for the labeling system (by 2024, most modern consumer goods are expected to be labeled within it).
In terms of its main characteristics, the standard is very similar to QR, and the codes are similar in appearance. DataMatrix code has almost the same level of security - when data is read when up to 30% of the code surface is damaged.
DataMatrix is recognizable by two perpendicular lines along the right and bottom edges. One of the advantages of the code is the ability to form it not only in square, but also in rectangular form.
- Aztec.
This two-dimensional code is recognizable by the “eye” in the very center - in the form of several squares enclosed in each other. In terms of its purpose and characteristics, it is also very similar to QR and DataMatrix, but has a unique advantage - in the form of adaptability to reading if, in some cases, up to 90% of the surface is damaged. True, you should focus on this indicator only if the volume of recorded data is not too large. If it is the same 2-3 KB, then error correction is usually possible if the code is damaged by no more than the same 30%.
The code is perfectly adapted to reading at a large angle: the scanner is guided by the “eye” and other corrective elements.
Another feature of the code is the ability to place it on an object without providing empty space between the edges of the code and other graphic objects. Relatively speaking, the code can be placed at the very edge of the identified object.
Now let’s get acquainted with practical tools for decoding (and “encrypting”) one-dimensional and two-dimensional barcodes.
Technical requirements for applying symbols
In order for the device to correctly recognize the encoding, you must comply with all recommended sizes and colors.
Among the important parameters:
- image width – 37.29 mm;
- its height is 25.93 mm;
- maximum stroke – 22.85 mm;
- the free part on the left side is 3.63 mm, on the right side – 2.31 mm;
- the line stops should be 1.65 mm longer;
- figures not exceeding 2.72 mm.
You can reduce it by no more than 20%, increase it by a maximum of 200%.