Thermal paste is a paste-like substance used in electronics to cool heating components . Most often found in laptops and desktop computers. Designed to improve heat transfer from the chip (central or graphics processor, memory modules, chipset, etc.) to the heatsink.
Displaces air from microscopic cavities between the heat distribution cover of the chip or the crystal itself and the heatsink. To ensure that the thermal conductivity of the thermal interface does not decrease, it must be stored in proper conditions.
What is regulated
GOST 19783-74 “Organosilicon heat-conducting paste. Technical Specifications" establishes requirements for the composition, safety, test methods of KPT-8, the warranty period is 1.5 years. The manufacturer determines the period of use based on the composition and quality of the product.
| Stamps Dear readers! To solve your problem right now, get a free consultation — contact the lawyer on duty in the online chat on the right or call: +7 (499) 938 6124 — Moscow and region. | Term validity (months) | |||
| In a syringe | In a tube | |||
| Open | Closed | Open | Closed | |
| KPT-8 | — | — | 36 | 36 |
| Arctic mx2, 4 | — | — | 96 | 96 |
| Alsil-3 | 36 | 36 | — | — |
| Alsil-5 | 60 | 60 | — | — |
| Cooler Master | — | — | 24 | 24 |
Shelf life according to GOST
Any thermal component has a certain shelf life during use and when sealed. When this time expires, the quality of the thermal paste may not meet the standards. It can dry out and lose thermal conductivity. Therefore, its further use may become impossible. If you try to use hardened thermal paste, it will not lead to anything good. Not only the processor can fail, but also the video card, power supply and other expensive PC components.
According to GOST 19783 - 74, which describes the storage conditions of organosilicon thermal conductive paste, and also establishes requirements for its quality, composition and safe use, its guaranteed shelf life is 18 months.
The manufacturer must set the service life of its products based on its characteristics and quality.
What period of life
Thermal paste performs an important function for preserving the technical capabilities of the computer - it evenly distributes heat between the PC elements, protecting them from excessive heating.
IMPORTANT! The characteristics of the product must be appropriate. This is the only way to ensure high-quality thermal conductivity.
The expiration date is set by the manufacturer. The main enemy is the action of air. Because of this, the thermal conductivity properties are rapidly lost, so it is strictly forbidden to keep the packaging opened.
If airtightness and other storage parameters are ensured, the service life of the new and already opened gel will be the same. For different brands it ranges from 2 to 8 years.
The product is available in a syringe or tube. Packaging does not have a significant impact on the service life of the contents; it depends more on the composition.
In a syringe
A common brand of paste produced in a syringe is Alsil-3, 5. This worthy representative of the segment can be used for 3 to 5 years.
In a tube
KPT-8, Cooler M, Titan Silver pastes are sold in tubes. They are good for 2-3 years. The quality is not inferior to goods in other containers.
ADVICE! The packaging of the paste is chosen based on personal preference and convenience. It does not affect the quality and shelf life.
How and where should it be stored?
The main thing when storing thermal paste is to avoid exposure to air , since contact with air can cause the paste to deteriorate. It is also better not to expose the paste to high temperatures and sunlight to avoid possible spoilage.
The ideal storage conditions for thermal paste are a dark place and room temperature.
When properly stored, pastes based on zinc or silver can retain their thermal conductivity properties for a very long time; for the best representatives of the thermal paste market, this period is up to 10 years from the date of production.
Popular varieties
Depending on the composition and packaging, the manufacturer guarantees different retention times for thermal conductivity properties. The following types of thermal pastes are most common in Russia:
- Alsil-3, 5 reflect the time of use in the name: 3 years and 5 years, respectively, sold in a syringe.
- KPT-8 can be used for 3 years, packaged in tubes.
- Arctic mx 2, 4 have the most durable characteristics and will last 8 years.
- Titan SG is a specific gel from a Chinese manufacturer of PC components. Does not indicate a specific time frame, comes with coolers or radiators.
- Cooler retains its properties for 2 years.
How often should you change thermal paste?
Look at this article and this one. The first is, in fact, about temperatures, and the second is about testing for stability and, again, temperatures under load.
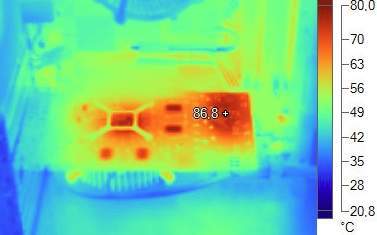
If the temperature regime is maintained normally, i.e. there is no overheating or its signs, and the temperature does not even creep close to critical, then there is no need to change the thermal paste often, i.e. this can be done once every six months or a year or less (depending on the method and time operation of a computer or laptop).
If you observe constant overheating or its signs (reboots, etc.), do not pass stability tests, etc., then you need to not only change the thermal paste more often, but also think about a good cooling system, in particular the case.
That's all, let's move on to the afterword.
How long does it take to change the thermal paste on the processor?
This is a substance with a gel consistency, which is designed to effectively conduct heat between elements of equipment and fill microcracks. It consists of:
- metals (copper, silver);
- boron, aluminum;
- diamond inclusions.
To effectively protect the processor from overheating, it must fully comply with the characteristics declared by the manufacturer. The need for an update will largely depend on the intensity of use of the computer and its technical features: temperature changes, brand and model.
There is no set time frame for replacement.
Every PC user should carefully monitor the operation of the device. If the processor heats up noticeably, you need to apply a new layer of the substance. Typically, this procedure is performed once every 2 years.
Comparison
At one time, a couple of models were compared and tested in thermal conductivity testing. So, among them were “Alsil-3” and “Alsil-5”. The first option is presented in a more liquid state of white color. There are no problems with application to the processor. The substance contains micropowder of aluminum nitride, so that the paste has viscous characteristics, silicone is added. A version was sold in a syringe with 3 grams. The cost is up to 100 rubles, and the shelf life of the thermal paste is 5 years. Alsil-5 is not exactly our client. It belongs to hot melt adhesives. In terms of thermal conductivity, it is slightly better than the previous version, but for the average user the difference is small.
The next example is KPT-8, which we have already discussed. This is the most famous option among all domestic models. It was supplied both in a tube and in a syringe. The manufacturer indicated that the shelf life was 5 years, but in fact, if you got a successful copy, it lasted more than 10 years. It is also very cheap, 60-70 rubles.
The best pastes reviewed are foreign options. It is especially convenient when a tube of this substance is supplied with the processor. Among these there are excellent options from Gigabyte, which are found in boxes with coolers from the company. Moreover, there are even several options under this brand, they differ in color and some characteristics.

Another company also performed well. The expiration date of Titan thermal paste is not difficult to determine. All information is on the tube, on average it is also 3-5 years. Thermal paste is usually included with coolers from this manufacturer. It can be used both for the processor and for other components, if required.
Now the situation with the purchase of foreign branded products has become freer. Finding options from Zalman or Fanner has become much easier than ten years ago. You will be especially lucky if you decide to buy a processor cooler, and a tube of high-quality thermal paste will be waiting for you in the box.
How to find out what has gone bad
Only a specialist can tell about the preservation of the thermal conductivity properties of the paste after laboratory testing. However, it is quite easy to identify a damaged product based on external signs. You should not use a gel that:
- separated into fractions (liquid and suspension);
- dried up;
- became lumpy;
- changed color, consistency, thickened.
IMPORTANT! After the expiration date, thermal paste will not be able to fully perform its functions.
How can you tell if it has gone bad?
Even after the expiration date stated by the manufacturer, thermal paste can still be used and applied to the surfaces of components.
And if the heat-conducting properties cannot be checked visually, then the consistency of the paste can indicate whether it has deteriorated or not. External signs of damaged thermal paste are:
- separation into components with different densities (suspension and liquid);
- the paste is dry;
- lumps have formed in it;
- thickening and other changes in consistency and color recorded visually.
Even a change in the consistency of thermal paste, such as delamination, does not clearly indicate that it has deteriorated, since stirring the paste will return it to its original state.
However, it is better not to take risks, since the heat-conducting functions of such thermal paste may be impaired.
The difference in operating temperatures of computer components with properly functioning high-quality thermal paste and damaged ones can be tens of degrees Celsius.
High component temperatures not only reduce the performance of a computer or other equipment, but can also lead to device failure, for example, a video card burnout.
Thermal paste is one of the plastic substances necessary for proper operation of computer components, which needs to be replaced in computers from time to time.
In order not to make a mistake in choosing thermal paste, you should choose it not only by price, but also by the indicated expiration dates, since its one-time consumption is not large, but replacing thermal paste on powerful modern devices is required quite often.
The best offers on the market can be stored at home for up to 5-8 years without losing the quality of the product.
Is it possible and how can I return a laptop within 14 days if I don’t like it? Read about it.
You can learn about what thermal paste is, why and how often you need to change it from the video:
Thermal paste is a material that can be stored for many years without losing its thermal conductivity properties.
You need to know how to properly maintain and use it to protect your computer from overheating.
How long is it stored: is there an expiration date, what is it?
All products have an expiration date In the case of thermal paste, this applies to both those already applied to computer components that generate heat, and those not yet unopened.
Over time, the product loses its ability to conduct heat and may dry out , which is unsafe for important computer components and can lead to their failure.
The shelf life is directly influenced by the composition and production technology of the heat-conducting paste.
A characteristic feature of the paste is that it should not lose its properties both after opening the package and after application to the surface.
Russian and Chinese products have become widespread on the market .
- Thermal pastes in a syringe from the domestic manufacturer Alsil-3 and Alsil-5 have a service life of 3 and 5 years, respectively.
Which thermal paste to choose
Nowadays it’s not a problem to find a good thermal paste that will last for several years in a row. Nowadays it is much more difficult to choose the right genuine composition. Often, even buying a new tube results in the user unpacking it, starting to apply it to the processor, and the substance immediately crumbles and crumbles. It also happens that the application process went fine, and after a couple of months you began to notice that the system is slowing down, you get to the processor and see that its temperature is increased. You open the case, and there was no thermal paste: it had dried out and crumbled.
Unfortunately, no one is safe from such terrible things. Recently, users have begun to observe how a massive substitution of the domestic product KPT-8 and Alsil-3 is taking place. Both pastes were previously created by the same manufacturer, but now when purchasing somewhere on unofficial sites or in China, the user receives a damaged product, which at first glance looks normal, but in reality it needs to be changed once a month, which, of course, is not good.
To choose thermal paste, it is better to consult with friends. Surely you had friends who had already bought this substance. They could check the quality of this model on their own PC and advise you. Also, purchasing foreign options from branded cooling and peripheral manufacturers Zalman and Gigabyte will bring you only a high-quality option. But it will cost you many times more than a domestic one.

What is thermal paste for?
Its main task is to ensure tight contact and good thermal conductivity in the place where the top cover of the processor comes into contact with the surface of the heatsink.
It is worth understanding that in most cases, replacing thermal paste involves cleaning the fans and the entire cooling system.
The better the thermal paste’s heat-conducting properties, the faster it will transfer heat from the processor to the radiator, from which the heat is then “blown away” by the fan. Thus ensuring lower operating temperatures of the processor. And this, in turn, will significantly extend the life of the processor and ensure its uninterrupted operation more reliably.
Applying thermal paste to the processor
It is worth considering that all laptops released since 2021 have soldered processors. That is, they do not change in the usual way. And if such a processor fails, repairs will be expensive (80-120 euros), and very often simply not practical. It may be cheaper to buy a new laptop.
Therefore, replacing thermal paste in a laptop and cleaning it from dust should be taken seriously.
Testing thermal pastes
I think everyone knows what thermal paste is and how to use it. However, if a person is assembling a computer for the first time, then I will explain a couple of points especially for him.
Firstly, thermal paste is needed to improve heat transfer from the processor to the heatsink. Even if the surface of the radiator looks smooth, in fact there may be places with a small air gap (due to poor processing/polishing of the metal surface). In this place, the processor heats up more, local overheating occurs and, at best, the processor freezes.
They often say that my radiator is polished to a mirror, so I don’t have to use paste. What can you say in response? The paste must be used in any case! After all, the surface of the processor, although seemingly smooth, is not polished. And in the case of a slight concavity, an unfortunate air gap appears. That is, it turns out that pasta is never superfluous. Even in the case of two ideal surfaces (I remember how I used fine sandpaper to bring (grind) the Celeron 366 processor to an ideal plane :), the excess paste will simply be squeezed out. By the way, it is best to apply the paste in a very thin, even layer.
So who's in the competition? Firstly, domestic paste KPT-8, which is sold always and everywhere. Secondly, another domestic paste Alsil-3, which is not so common (I had to go to another city for it :), but is loved by overclockers. The third participant in the test is a silvery-looking Titan Silver Grease paste, a syringe of which is found in every box with a Titan cooler. A couple more famous pastes: one is called “High Performance”, the other is “Premium”. And finally, we will test the paste from the Zalman cooler.
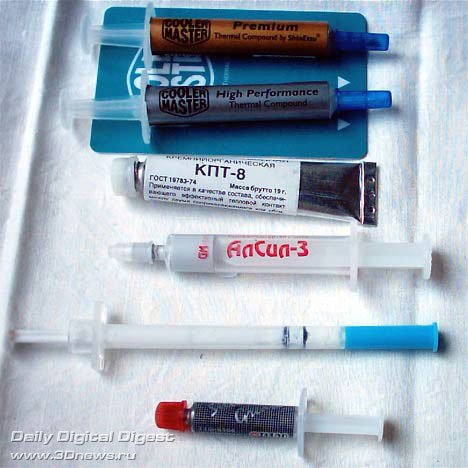
I will not give the chemical composition of the pastes participating in the review, since the average reader is only interested in questions related to use: which paste is best applied, removed, and with which paste cooling the processor is most effective.
Alsil3
So, Alsil3 paste is a fairly liquid white paste that is easy to apply and remove from the surface of the processor. Manufacturer: domestic company GM-Inform. Sold in a syringe, net weight 3 grams, the cost is about 35 rubles.
KPT8
Another Russian-made paste is organosilicon KPT8. Sold in a metal tube (gross weight 19 grams), . The shelf life is 5 years, and this tube, even with active home use, will last for a much longer period. For example, I have been using one tube for more than 4 years. In this regard, for fun, I tested the paste released in 2002 and the remains of the paste released back in 1998. The paste is white, the same liquid as Alsil3 (the old paste is somewhat thicker), easy to apply and remove.
Cooler Master
The next contenders for victory are a couple of pastes from Cooler Master. There were no complaints about the first one, with the name “High performance” - the paste is similar in all its properties to KPT8, but the second one - “Premium” quite puzzled me.
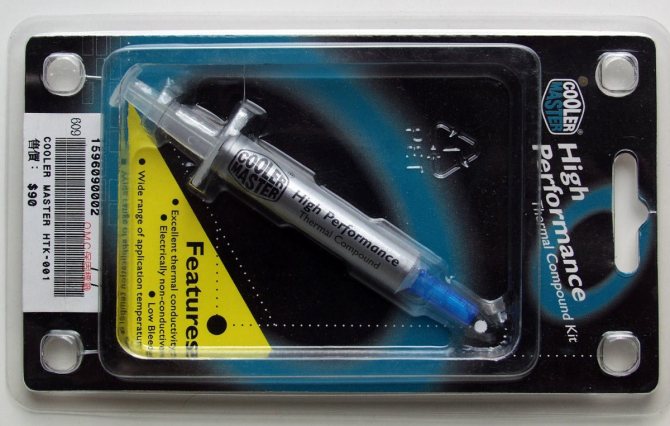

Cooler Master "High performance"
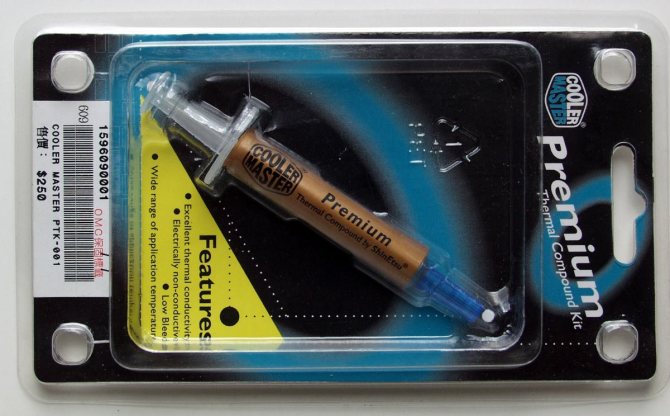

Cooler Master "Premium"
It looks very likely that it was lying in a warehouse somewhere for a very long time, since its condition did not make it possible to distribute it evenly over the surface of the processor. The paste lay out in clumps and did not smear at all. At the same time, the paste looks silvery, but I have serious doubts that this noble metal was used in its production. There are only 1.6 grams in a tube (2 grams in a “High performance” tube). And, in order not to upset the buyer with this fact, the entire tube is wrapped in a paper sticker. The paste is sold in a beautiful transparent package and along with the paste there is a plastic card for uniform application of the paste and strange pieces of paper with Socket423 and Socket370 stencils (the other connectors are for processors, apparently the paste is not suitable :-).
Finally, it’s worth adding that these pastes are not sold in Russia, but were brought by us from our last trip to Computex. Prices on the packages are indicated in “New Taiwanese dollars,” which have the strange property of coinciding with Russian rubles on a penny-to-kopeck basis. Those. “High performance” costs 90 rubles, and “Premium” costs as much as 250 rubles.
Titan Silver Grease
Let's move on to Titan Silver Grease paste (TTG-S104). The silver-based paste looks thick and applies more or less well. But removing it from the processor is not an easy task. In the case of the Pentium4, everything is simple - the paste is easily removed from the copper cover (heat spreader - Integrated Heat Spreader) using a soft cloth. But from AMD processors, the paste is removed only from the core, and the paste can only be removed from the processor substrate using some kind of liquid (I don’t know, I won’t advise). Regular attempts to remove the paste using a soft cloth only result in the paste smearing. By the way, it looks like the paste is conductive and needs to be used very carefully. The paste is in a syringe, weight 1.5 grams.
Paste from Zalman CNPS3100+
And finally, the paste from the Zalman CNPS3100+ copper cooler, the paste is in a syringe (the aluminum-copper cooler comes with a small tube). Its properties are similar to KPT8 paste.
So, the pastes act as an orderly line of syringes. And to meet them are thermal interfaces, which are usually applied to the surface of radiators. Let me list the participants: Bergquist 225U (usually found on Thermaltake coolers), thermal interface from a boxed cooler and an Elan Vital cooler.
Testing
All thermal pastes were tested with a Thermaltake Volcano 7+ cooler, with the rotation speed reduced to 2700 rpm (even at this speed the cooler is very efficient!). But the temperature indicators of native thermal interfaces are relative values. Those. For example, I took an Elan Vital cooler, tested it with the original blotch, then cleaned off this interface (I will remember this process with an unkind word for a long time :), after which I tested it with KPT8 paste. The difference was 7 degrees C, in favor of the latter. Here in the diagram, the result of the thermal interface of the Elan Vital cooler was adjusted by 7 degrees C.
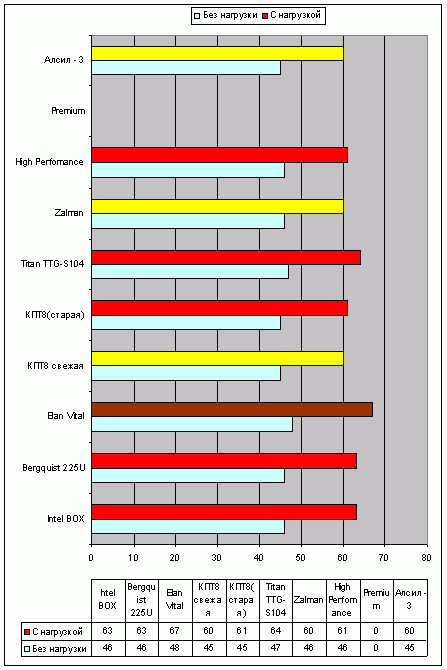
So, the results: the winners were pastes KPT8, Alsil3 and paste from the Zalman cooler. They all showed the same result (maybe there is a difference in tenths, but it doesn’t matter). The CoolerMaster paste showed the second result, with a difference of only one degree C. The old KPT8 paste showed the same lag, i.e. Over time, the paste loses its quality. And finally, Titan paste came in last place, with a lag of 4 degrees C. As they rightly say, “all that glitters is not silver :).”
Which paste to choose among the leaders, CBT or Alsil? The first is supported by its prevalence and low cost, but CBT has one unpleasant drawback. At high temperatures it dries and its thermal conductivity properties deteriorate. Often, when removing the cooler from the processor after a couple of months of operation, I found dry powder instead of paste. Alsil3 paste, on the contrary, according to the manufacturer, is made on a non-drying basis, which makes regular replacement of the paste unnecessary.
As for thermal interfaces, although they showed worse results than thermal pastes, the lag was small. And for a system without overclocking the processor, you can safely use coolers with a native thermal interface.
Additional materials:
Comparison of coolers for P4. Q4 `2002 Comparison of coolers for the SocketA connector. Q4 `2002 Comparison of coolers for P4. Q3 `2002 Comparison of coolers for the SocketA connector. Q3 `2002 Comparison of coolers for the SocketA connector. Q2 `2002 “Master” of cooling Badong Encyclopedia of processor coolers Testing thermal pastes Coolers with aluminum fans. Titan vs Spire Advanced CPU Cooling Technologies
What to do with the expired one?
Thermal conductive paste is necessary for the correct and efficient operation of computer components.
The difference between the operating temperatures of computer components with high-quality thermal paste and damaged ones can be tens of degrees Celsius.
Using an expired product in a PC can lead to overheating and subsequent failure of processors, power supplies, video cards, etc. So does it make sense to risk the performance of your computer or laptop?
See also in this video all about thermal paste:
Didn't find the answer to your question? Find out how to solve exactly your problem - call right now:
It's fast and free!
Thermal paste is widely used in the electronics industry; it transfers heat from the surface to be cooled (computer components) to heat dissipating devices (radiators).
For the buyer, not only the warranty on thermal paste is important, that is, how long it retains its properties after application, but also the shelf life in the original container . We’ll talk about the shelf life of popular thermal paste in this article.
Dear readers! Our articles talk about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is unique.
If you want to find out how to solve your particular problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right or call the free consultation numbers:
—>
Is it possible to get a tax deduction for training in a driving school? Find out the answer right now.
What is this?
Before moving on to how to find out the expiration date of thermal paste, you need to understand what it is and what its purpose is. So, thermal paste is a kind of “ointment” for a computer, which has a heat-removing composition that promotes effective heat transfer between the element that heats up and the radiator. As a result, if there is a high load on the processor or video card, so that they do not burn out, this heat is removed through the thermal paste and radiator, and then accelerated by the cooler.

This substance is often represented by a homogeneous mass of white or gray color. Sometimes there are silver or blue shades.
How long is it stored: is there an expiration date, what is it?
All products have an expiration date In the case of thermal paste, this applies to both those already applied to computer components that generate heat, and those not yet unopened.
Over time, the product loses its ability to conduct heat and may dry out , which is unsafe for important computer components and can lead to their failure.
The shelf life is directly influenced by the composition and production technology of the heat-conducting paste.
A characteristic feature of the paste is that it should not lose its properties both after opening the package and after application to the surface.
Russian and Chinese products have become widespread on the market .
- Thermal pastes in a syringe from the domestic manufacturer Alsil-3 and Alsil-5 have a service life of 3 and 5 years, respectively.
What to do with the expired one?
Thermal conductive paste is necessary for the correct and efficient operation of computer components.
The difference between the operating temperatures of computer components with high-quality thermal paste and damaged ones can be tens of degrees Celsius.
Using an expired product in a PC can lead to overheating and subsequent failure of processors, power supplies, video cards, etc. So does it make sense to risk the performance of your computer or laptop?