Parameters for turning on the heating
Heating is supplied in accordance with the standards prescribed in Decree No. 354 of 2011.
It contains information that heat is supplied to apartment buildings at an air temperature outside the window of +8°C, which persists for 5 days. If there are changes in temperature, the radiators will remain cold.
IMPORTANT! The heating is turned on only on the sixth day. Basically, in all regions, the heating season begins on October 15 and lasts until April 15.
What do the calculated indicators depend on?
First of all, it depends on the air temperature. Design data is also taken into account when building a house. A variety of building materials used for construction have distinctive characteristics, including thermal conductivity. The influence of climatic conditions is directly related to the volume and quality of heat supply services provided. There were cases when local authorities established the same fee for everyone in a locality, but the court considered such actions to be unlawful. Housing built of wood, one or two stories high, requires a completely different heating method than high-rise brick or block buildings.
For no more than three years, the standards remain unchanged. A number of exceptions are provided: major home renovations, which entail changes in temperature conditions. Or adjustments are made to the current Rules. Or a change in climate conditions.
Temperature standards
The heating circuit of a residential multi-storey building interacts with a centralized system to which pipes are connected. Through them, water flows into the apartment building, where it is subsequently regulated by valves.
Then it flows through the risers into the radiators and radiators of each living space. The heating system coolant parameters are established by regulations. As a rule, it should be brought to a temperature of 130-150°C.
But this indicator is affected by the temperature outside. Basically, the water temperature at the boiler outlet is 115°C. According to regulations, the temperature in the heating system can be 95-105°C. In order for comfortable conditions to be created in the apartment, the proper condition of the parameters of the riser through which water from the heating unit is delivered to the apartment must be ensured. Depending on the season, parameters may vary. In winter, the riser should be heated to 70-90°C.
How is the standard calculated?
This indicator is included in the receipt for those who do not use a personal meter, which helps control readings. Data is calculated based on costs in previous seasons. The amount of heat energy expended is divided by the number of heated square meters and divided into twelve months. Thus, a value is obtained indicating how much you need to pay per square meter of living space. This figure is multiplied by the area of the premises and the regional special tariff. The calculation is made on the basis of the Rules for Establishing and Determining Standards for the Consumption of Utilities, approved by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 306 of May 23, 2006. (ed. dated February 27, 2017)[2].
Apartment owners who have their own measuring device pay only for the volume of services consumed specifically for their living space.
The installed common house heat meter, although it reduces the payment, but provides for the addition of a fee for general service to the bills. The amount of utility resources provided to residents for heating an apartment building is distributed among all residents in proportion to the square footage of the apartment. Payments are also made for maintaining the required temperature in hallways and basements. It is also worth considering that some of the heat is lost during its passage through underground communications. Each building has its own characteristics and costs may differ even in neighboring buildings.
Air in the apartment
There are uniform standards that determine the heat index in a residential area. According to them, during the heating period the apartment must maintain the following temperature regime:
- In the living room - +18°C.
- In the corner living room - +20°C.
- In the bathroom at least +25°C.
- In the toilet (if located separately from the bathroom) - +18°C.
- If the bathroom is combined - + 25°C.
- In the kitchen at least +18°C.
The standards are established according to GOST. They are designed to preserve the health of residents. Common premises also have their own standards. The indicators should be:
- Entrance — +16°С.
- Elevator - +5°C.
- Attic and basement - +4°С.
If the actual parameters do not meet the standards, you should contact the heating network. These circumstances make it possible to reduce heating payments by 0.15% for each hour of deviation.
Additional influencing factors
The coolant temperatures themselves are also directly influenced by such equally significant factors as:
- A decrease in temperatures outside, which entails a similar decrease indoors;
- Wind speed - the higher it is, the greater the heat loss through the front door and windows;
- The tightness of walls and joints (installation of metal-plastic windows and insulation of facades significantly affects heat retention).
For their part, construction companies understand that the costs they incurred for insulating facilities will be fully and soon recouped. This is also beneficial for owners, since utility bills are very high, and if you pay, it is really for the heat received and stored, and not for its loss due to insufficient insulation of the premises.
Radiator temperature
However, regardless of the weather conditions outside the room and how insulated it is, the most important role is still played by the heat transfer of the radiator. Typically, temperatures in central heating systems range from 70 to 90 degrees.
However, it is important to take into account that this criterion is not the only one in order to have the desired temperature regime, especially in residential premises, where the temperatures in each individual room should not be the same, depending on the intended purpose.

Those rooms that are intended for children must have a temperature limit of 18 to 23 degrees, depending on what they are intended for. So in the pool it cannot be less than 30 degrees, and on the veranda it must be at least 12 degrees.
Speaking about a school educational institution, it should not be below 21 degrees, and in the bedroom of a boarding school - at least 16 degrees. For a public cultural institution, the norm is from 16 degrees to 21, and for a library - no more than 18 degrees.
What affects battery temperature?
In addition to the thermal output of the coolant and the temperatures outside, the heat in the room also depends on the activity of the people inside. The more movements a person makes, the lower the temperature can be and vice versa.
This is also necessarily taken into account when distributing heat. As an example, we can take any sports institution where people are a priori in active movement. It is not advisable to maintain high temperatures here, as this will cause discomfort.
Accordingly, an indicator of 18 degrees is optimal.
It can be noted that the thermal performance of batteries inside any premises is affected not only by the outside air temperature and wind speed, but also by:

A variety of heating systems - for single-pipe systems the norm is 105 degrees, for two-pipe systems - 95 degrees. At the same time, it is not permissible for the difference in the heat removal and heat supply systems to exceed 105-700 and 95-700 degrees, respectively;- The direction of flow of coolants on the radiator batteries - with the upper wiring, the difference can be 20 degrees, and with the lower – 30;
- A variety of heating devices - radiators and convectors - have different thermal output, respectively, and their temperature conditions are different (the heat output of a convector is lower than that of a radiator).
Approved schedules
Since the temperature outside has a direct impact on the heat inside, a special temperature schedule has been approved.
Outside temperature indicatorsWater inlet, °СWater in the heating system, °СWater outlet, °С
| 8 °C | from 51 to 52 | 42-45 | from 34 to 40 |
| 7 °C | from 51 to 55 | 44-47 | from 35 to 41 |
| 6 °C | from 53 to 57 | 45-49 | from 36 to 46 |
| 5 °C | from 55 to 59 | 47-50 | from 37 to 44 |
| 4 °C | from 57 to 61 | 48-52 | from 38 to 45 |
| 3 °C | from 59 to 64 | 50-54 | from 39 to 47 |
| 2 °C | from 61 to 66 | 51-56 | from 40 to 48 |
| 1 °C | from 63 to 69 | 53-57 | from 41 to 50 |
| 0 °C | from 65 to 71 | 55-59 | from 42 to 51 |
| -1 °C | from 67 to 73 | 56-61 | from 43 to 52 |
| -2 °C | from 69 to 76 | 58-62 | from 44 to 54 |
| -3 °C | from 71 to 78 | 59-64 | from 45 to 55 |
| -4 °C | from 73 to 80 | 61-66 | from 45 to 56 |
| -5 °C | from 75 to 82 | 62-67 | from 46 to 57 |
| -6 °C | from 77 to 85 | 64-69 | from 47 to 59 |
| -7 °C | from 79 to 87 | 65-71 | from 48 to 62 |
| -8 °C | from 80 to 89 | 66-72 | from 49 to 61 |
| -9 °C | from 82 to 92 | 66-72 | from 49 to 63 |
| -10 °C | from 86 to 94 | 69-75 | from 50 to 64 |
| -11 °C | from 86 to 96 | 71-77 | from 51 to 65 |
| -12 °C | from 88 to 98 | 72-79 | from 59 to 66 |
| -13 °C | from 90 to 101 | 74-80 | from 53 to 68 |
| -14 °C | from 92 to 103 | 75-82 | from 54 to 69 |
| -15 °C | from 93 to 105 | 76-83 | from 54 to 70 |
| -16 °C | from 95 to 107 | 79-86 | from 56 to 72 |
| -17 °C | from 97 to 109 | 79-86 | from 56 to 72 |
| -18 °C | from 99 to 112 | 81-88 | from 56 to 74 |
| -19 °C | from 101 to 114 | 82-90 | from 57 to 75 |
| -20 °C | from 102 to 116 | 83-91 | from 58 to 76 |
| -21 °C | from 104 to 118 | 85-93 | from 59 to 77 |
| -22 °C | from 106 to 120 | 88-94 | from 59 to 78 |
| -23 °C | from 108 to 123 | 87-96 | from 60 to 80 |
| -24 °C | from 109 to 125 | 89-97 | from 61 to 81 |
| -25 °C | from 112 to 128 | 90-98 | from 62 to 82 |
| -26 °C | from 112 to 128 | 91-99 | from 62 to 83 |
| -27 °C | from 114 to 130 | 92-101 | from 63 to 84 |
| -28 °C | from 116 to 134 | 94-103 | from 64 to 86 |
| -29 °C | from 118 to 136 | 96-105 | from 64 to 87 |
| -30 °C | from 120 to 138 | 97-106 | from 67 to 88 |
| -31 °C | from 122 to 140 | 98-108 | from 66 to 89 |
| -32 °C | from 123 to 142 | 100-109 | from 66 to 93 |
| -33 °C | from 125 to 144 | 101-111 | from 67 to 91 |
| -34 °C | from 127 to 146 | 102-112 | from 68 to 92 |
| -35 °C | from 129 to 149 | 104-114 | from 69 to 94 |
Batteries
The heating of a living space is influenced by many factors: technical characteristics, thermal conductivity, installation of batteries, etc. Their correct installation and operation will create the necessary conditions for heating radiators in living rooms to comply with current standards.
It is worth paying attention to the number of battery sections. A coolant heated to the same temperature with a different number of sections will heat differently.
What is meant by heating standards?
The norm is understood as the temperature range at which the activation of compensatory mechanisms of heating or cooling does not occur. It should be noted that most people feel comfortable when the temperature is in the range from +21 to +25 degrees.
This indicator is somewhat different for different population groups. For example, according to research, the optimal air temperature in an apartment for children and women is +23-25 degrees. And for men these values are slightly lower and range from +21-23 degrees. Psychologists and hygienists have identified heating standards in an apartment at which a person feels best - this is 18-24 degrees above zero. Therefore, the minimum possible room temperature is +18 degrees.
It is at this value that a person can stay in the house for a long time without outer clothing and without harming his health. Heating standards in an apartment are regulated by law. During the cold period, certain climatic parameters must be maintained in residential buildings and apartments. All this is described in detail in the documentation. According to the norms, heating payments are also calculated. In different cases, standards are set differently.
Since heating parameters in an apartment depend on three factors:
- Climatic features of the region of the country.
- Type of heating: centralized or autonomous. In the first case, to calculate the standard, the location of the apartment is taken into account. For example, corner or not. The coolant temperature is also taken into account. In the second case, the concept of norm is somewhat conditional. It all depends on the comfort of living and the heating boiler.
- Type of heated room.
Minimum
Very often, when the heating is on, residents complain about a lack of heat. The main reason is the discrepancy between the standard temperature of the radiators and the actual one. Airiness of the system can influence this fact.
If the fault is the unusable condition of the battery or pipe, they will need to be replaced. In this situation, while the heating system is inoperative, apartment residents should not pay for heating.
The minimum standard temperature for batteries has not been determined, so you need to focus on the heating of the air in the apartment. The temperature standards for living rooms in an apartment building should be +16-+25°C. If it does not meet the standards, a specialist from the heat supply company is called to the house.
EFFECT OF TEMPERATURE ON COOLANT CHARACTERISTICS
In addition to the factors listed above, the temperature of the water in the heating pipes affects its characteristics. The method of functioning of gravity heating systems is based on this. As the water heating value increases, it expands and circulation appears.
COOLANTS FOR HEATING SYSTEMS
But when using antifreeze, exceeding normal temperatures in radiators can lead to different results. Therefore, for heating with a coolant other than water, it is necessary to first determine the permissible heating values. This does not apply to the temperature of the central heating radiators in the apartment, since such devices do not use antifreeze-based liquids.
Antifreeze is used if there is a risk of exposure to low temperatures on radiators. Unlike water, it does not change from liquid to crystalline at 0 degrees. But if the heat supply operation exceeds the norms of the temperature table for heating to a greater extent, the following phenomena may be observed:
- foaming This contributes to an increase in coolant volume and pressure level. There will be no reverse process when the antifreeze cools;
- the appearance of limescale. Antifreeze contains mineral components. If the heating temperature in the apartment is violated, they precipitate. Over time, this leads to clogged pipes and radiators;
- increase in density. Malfunctions of the circulation pump may occur if its rated power was not designed to handle such situations.
Therefore, it is much easier to monitor the water temperature in the heating system of a private home than to control the heating level of antifreeze. Moreover, substances based on ethylene glycol emit gases that are harmful to humans when evaporated.
Today they are almost never used as a coolant in autonomous heating systems. Before using antifreeze in heating, it is necessary to replace all rubber seals with paranitic ones. This is due to the high level of permeability of this type of coolant.
OPTIONS FOR NORMALIZING HEATING TEMPERATURE CONDITIONS
Minimum water temperatures in the heating system are not considered the main threat to its operation. This affects the microclimate in living rooms, but does not affect the operation of the heating supply. If the water heating norm is exceeded, emergency situations may occur.
SAFETY GROUP FOR AUTONOMOUS HEATING
When creating a heating scheme, you need to provide a list of measures aimed at preventing a critical increase in water temperature. First of all, this will lead to increased pressure and stress on the inside of pipes and radiators. If this happened once and lasted a short time, then the heating parts will not be damaged.
But such cases appear under the constant influence of specific factors. Most often this is the incorrect operation of a solid fuel boiler. To avoid breakdowns, it is necessary to upgrade the heating in the following way:
- installation of a security group. It consists of an air vent, a bleed valve and a pressure gauge. If the water temperature reaches a critical level, these parts will eliminate excess coolant, thereby ensuring normal circulation of the liquid for its natural cooling;
- mixing unit. It connects the return and supply pipes. Additionally, a two-way valve with a servo drive is mounted. The latter is connected to the temperature sensor. If the heating level exceeds the norm, the valve will open and a mixing of hot and cooled water flows will occur;
- electronic heating control unit. It distributes the water temperature in different parts of the system. If the thermal regime is violated, it sends a corresponding signal to the boiler processor to reduce power.
These measures will prevent improper heating operation at the initial stage of the problem. It is most difficult to control the water temperature in systems with a solid fuel boiler
Therefore, for them, special attention must be paid to the selection of indicators of the safety group and mixing unit
Maximum
Maximum heating rates in the apartment:
- If there is a two-pipe heating structure, the maximum possible temperature is +95°C.
- If the heating system is single-pipe, the temperature of the battery must be at least 115°C.
The recommended figure for optimal indicators is 85-90°C. If the mark reaches or exceeds 100°C, you must take the necessary measures to prevent the water in the heating system from boiling.
As a rule, during the production of radiators, the maximum permissible temperature threshold is indicated. But it is advisable to avoid strong heat to prevent damage to the radiator.
ATTENTION! The water temperature in the battery should be no more than 20°C, the temperature at which the material can ignite.
Features of calculating internal temperature in different rooms
The rules provide for maintaining the temperature for a living space at 18˚C , but there are some nuances in this matter.
- For a corner room of a residential building, the coolant must provide a temperature of 20˚C.
- The optimal temperature for a bathroom is 25˚C.
- It is important to know how many degrees there should be according to standards in rooms intended for children. The set temperature ranges from 18˚С to 23˚С. If this is a children's pool, you need to maintain the temperature at 30˚C.
- The minimum temperature allowed in schools is 21˚C.
- In establishments where cultural events take place, according to standards, a maximum temperature of 21˚C , but the figure should not fall below 16˚C.
To increase the temperature in the premises during sudden cold snaps or strong north winds, boiler room workers increase the degree of energy supply for heating networks.
The heat transfer of batteries is affected by the outside temperature, the type of heating system, the direction of coolant flow, the state of utility networks, and the type of heating device, the role of which can be played by either a radiator or a convector.
ATTENTION! The temperature delta between the radiator supply and return should not be significant. Otherwise, there will be a large difference in the coolant in different rooms and even apartments of a multi-story building.
The main factor, however, is the weather , which is why measuring the outside air to maintain a temperature schedule is a top priority.
If the temperature outside is down to 20˚C, the coolant in the radiator should be 67-77˚C, while the return rate is 70˚C.
If the street temperature is zero, the norm for the coolant is 40-45˚С, and for the return – 35-38˚С. It is worth noting that the temperature difference between supply and return is not large.
Measurement
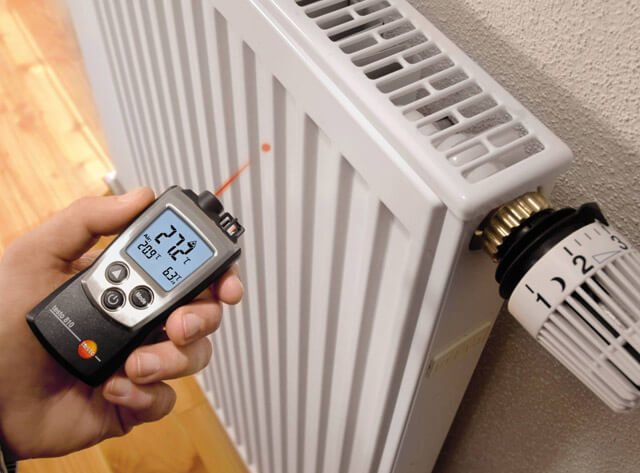
If apartment residents have doubts about the quality work of the heat supply company and the room is very cold, it is necessary to establish the cause of the poorly heated radiators. First of all, you will need to measure the temperature of the pipes, radiator, air in the room and the water itself in the heating system.
It must be borne in mind that self-conducted measurements cannot be presented as evidence of violation of standards. But based on them, you can file a complaint and subsequently invite employees of the service company for control measurements.
Timeframe for consideration of a claim
As a rule, the period for consideration of a claim is 10 days, but in this situation, when the apartment is not heated and it is cold outside, the management company should consider it faster. When filing a complaint, indicate that it must be reviewed within 2-3 days. During this time, they should send you a specialist who will measure the temperature of the battery and draw up a report on violations in the heating system.
If the fact of a violation is established and recorded in the report, then the day after the report is drawn up, workers should come to you to fix the heating problems.
Definition of water
It is impossible to measure the water temperature in a central heating system with reliable accuracy. Only air temperature can be determined most accurately. You can measure it as follows:
- Open the tap (provided that it is installed in the apartment).
- Place a container with a thermometer.
- Fill with water.
- Wait for the thermometer result.
A slight upward deviation of 4°C is allowed.
DHW
You can set the temperature in another way. Since batteries and hot water supply are interconnected, it is more advisable to measure the temperature through a hot tap.
To measure, place a container with a thermometer under running hot water. In a few minutes you can see the results. If the mark shows 60-75°C, the coolant meets the norm.
ATTENTION! If the temperature is lower, it means the water is not heated enough.
Radiator
Measuring their temperature is easy:
- You need to take a regular thermometer and apply it to the battery. Wait a few minutes until it warms up. Add 1-2 degrees to the result obtained.
- Measurement using an infrared thermometer. They have a small error and do not need to come into direct contact with the heating device. The result is quite fast.
- Use an electrical device with a sensor and a thermal lamp. By installing the sensor on the battery, the device will display the value.
Measuring battery temperature
If the apartment is cold, you can measure the temperature in the heating radiators.
You can do this in one of the following ways:
- using a thermometer - add 1-2 ℃ to the value obtained on the surface of the battery and obtain the temperature of the coolant;
- infrared thermometer;
- alcohol thermometer - the device is tied to the battery and wrapped in heat-insulating material to obtain more accurate data.
Accurate temperature readings can only be obtained if you use a device with a quality certificate with a range from 5 ℃ to 40 ℃ and an acceptable error of 0.1 ℃.

After comparing the obtained values with what the battery temperature should be and identifying discrepancies, you can contact the service organization. It will perform a control measurement of fluid temperatures in the heating circuit in a specific apartment.
As an option, you can measure the temperature of hot tap water - if it is supplied to the apartment. If a value in the range of 60-75 ℃ is obtained, then the norm is met, and all other values are already considered a deviation from it.
What to do
If there is a problem with cold batteries, you need to clarify whether it arose in a specific room or whether other residents also suffer from it. If the quality of heating does not meet the standards, you can file a collective or individual complaint:
- To a service organization (management company, construction cooperative, etc.).
- To the service provider.
- To the emergency dispatch service.
- Housing inspection.
Once accepted, the complaint must be registered. After which, they must establish the reason and draw up an act of violation. Based on this document, a recalculation is made for the period when there was no heat.
If there is no response to the complaint and no action is taken to correct problems in the heating system, you need to contact Rospotrebnadzor.
Why does the consumer need to know the coolant supply standards?
Payment for utilities in the heating column should depend on the temperature in the apartment provided by the supplier.
The temperature chart table, according to which the boiler should operate optimally, shows at what ambient temperature and by how much the boiler room should increase the energy level for heat sources in the house.
IMPORTANT! If the parameters of the temperature schedule are not met, the consumer may request a recalculation for utilities.
To measure the coolant value, you need to drain some water from the radiator and check its heat level. Thermal sensors and heat metering devices , which can be installed at home, are also successfully used
The sensor is mandatory equipment for both city boiler houses and ITPs (individual heating points).
Without such devices it is impossible to make the heating system work economically and productively. The coolant is also measured in DHW systems.
Temperature schedule for coolant supply to the heating system: SNIP 2021
The temperature of the water in the heating system depends on the air temperature outside and is maintained in it according to a special temperature schedule, which is calculated differently by specialists for different heat supply sources, depending on local weather conditions.
If you want to find out how to solve your specific problem, please contact the online consultant form on the right. It's fast and free! Or call us at :
As already mentioned, the temperature graph directly depends on the outside air temperature. Accordingly, the lower the air temperature, the greater the heat loss.
The question arises, what temperature indicator should be used in the calculation? This indicator has already been derived and can be found in regulatory documents.
It is based on the average temperature of the five coldest days of the year. In this case, a period of 50 years is taken, and the 8 coldest winters are selected.
Why is the average daily temperature calculated this way?
First of all, this makes it possible to be prepared for low temperatures during the winter season, which occur once every few years.
Also, taking this indicator into account, you can significantly save on costs when creating heating systems. If we consider this in the volume of mass construction, the amount that can be saved will be significant.
Of course, the temperature of the heated room will depend on the temperature of the coolant.

What temperature should the apartment be during the heating season?
Read about the normal temperature of batteries in an apartment here.
There are several other factors that also affect indoor temperature:
- The lower the air temperature outside, the lower it is indoors;
- Wind speed also affects the temperature. The stronger the wind loads, the more heat loss through window frames and entrance doors increases;
- How tightly are the joints in the walls of the house sealed? For example, insulation of the facade walls of a house or metal-plastic windows are factors that will affect the temperature inside the room.
Today, building codes have changed. Construction companies increase the value of their facilities through thermal insulation work, such as insulation of the facade of the house, basements, foundation, roof and roofing.
The costs of insulating a house are quite high, but this is a guarantee that in the future you will save on heating, since these measures reduce the cost of purchasing fuel.
How relevant is this today? Of course, it is for this reason that construction companies increase the cost of building houses, knowing that measures to insulate the house will, over time, pay off with interest.
Radiator temperature
Everything mentioned above is certainly important. But the main thing that affects the temperature in the rooms is the temperature of the radiator batteries. As a rule, the temperature in central heating systems ranges from 70 to 90 degrees.
Everyone knows that it is impossible to achieve the desired temperature inside a room using this criterion alone, taking into account the fact that the temperature in all rooms should be different, since each room has its own purpose:
- If the room is corner, then the temperature should not fall below + 20 0 C, and in other rooms the temperature is not lower than +18 0 C, in the shower room not lower than +25 0 C. If the temperature outside drops to -30 0 C or lower, then all the above indicators will increase to +22 0 C and 20 0 C, respectively;
- In rooms intended for children - from +18 0 C to +23 0 C. But even here the temperature regime depends on what this room is intended for. In the pools - not lower than +30 0 C, and on the verandas for walking - not lower than +12 0 C;
- In children's schools - not lower than 21 0 C, and in the bedrooms of boarding schools - not lower than 16 0 C;
- In cultural institutions the temperature ranges from 16 0 C to 21 0 C. For libraries - up to 18 0 C.
Temperature standards are approved for all premises depending on their purpose. The above is only a small part of a huge list.
The normal temperature in a room is affected by how intensely a person moves inside it. The fewer movements a person makes, the higher the temperature in the room should be.
The heat distribution is based on this. As evidence, in sports institutions where a person is on the move, it is not advisable to maintain the temperature at a high level; for this reason, the temperature there is no higher than +18 0 C.
Factors affecting battery temperature:
- Outside temperature;
- Type of heating system. For a single-pipe system, the standard temperature indicator is +105 0 C, and for a two-pipe system +95 0 C. The temperature difference in the supply and discharge system should not be higher than 105-70 0 C and 95-70 0 C, respectively;
- Direction of coolant flow to radiator batteries. If the wiring is from above, then the difference is 2 0 C, and if the wiring is from below, then 3 0 C;
- Type of heating device. Radiators and convectors have different heat output, which means the temperature regime is different. Radiators have higher heat transfer than convectors.
But still, everyone understands that heat transfer, be it a radiator or a convector, will depend on the temperature outside.
Depending on the outside temperature, the coolant temperature values are calculated and have the following values (these temperature indicators are rounded for convenience):
Economical energy consumption in the heating system can be achieved if certain requirements are met. One option is to have a temperature diagram, which reflects the ratio of the temperature emanating from the heating source to the external environment. The values of the values make it possible to optimally distribute heat and hot water to the consumer.
High-rise buildings are mainly connected to central heating. The sources that transmit thermal energy are boiler houses or thermal power plants. Water is used as a coolant. It is heated to a given temperature.
Having gone through a full cycle through the system, the coolant, already cooled, returns to the source and reheats. Sources are connected to consumers by heating networks. Since the environment changes temperature, thermal energy should be adjusted so that the consumer receives the required volume.
Heat regulation from the central system can be done in two ways:
- Quantitative. In this form, the water flow changes, but its temperature remains constant.
- Qualitative. The temperature of the liquid changes, but its flow does not change.
In our systems, the second regulation option is used, that is, qualitative. Here there is a direct relationship between two temperatures: the coolant and the environment. And the calculation is carried out in such a way as to ensure the heat in the room is 18 degrees and above.
Hence, we can say that the temperature graph of the source is a broken curve. The change in its directions depends on temperature differences (coolant and outside air).
The dependency schedule may vary.
A specific diagram has a dependency on:
- Technical and economic indicators.
- CHP or boiler room equipment.
- Climate.
Below is an example of a diagram, where T1 is the coolant temperature, Tnv is the outside air:
A diagram of the returned coolant is also used. A boiler house or thermal power plant can estimate the efficiency of the source using this scheme. It is considered high when the returned liquid arrives chilled.
This is interesting: Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation No. 731 of February 27, 2017, 2021
The stability of the scheme depends on the design values of fluid flow of high-rise buildings. If the flow through the heating circuit increases, the water will return uncooled, as the flow rate will increase. Conversely, with minimal flow, the return water will be sufficiently cooled.
The supplier's interest, of course, is in the supply of return water in a cooled state. But there are certain limits for reducing consumption, since a decrease leads to loss of heat. The consumer’s internal temperature in the apartment will begin to drop, which will lead to violation of building codes and discomfort for ordinary people.
The temperature curve depends on two quantities: outside air and coolant. Frosty weather leads to an increase in coolant temperature. When designing a central source, the size of the equipment, building and pipe size are taken into account.
The temperature leaving the boiler room is 90 degrees, so that at minus 23°C, the apartments are warm and have a value of 22°C. Then the return water returns to 70 degrees. Such standards correspond to normal and comfortable living in the house.
Analysis and adjustment of operating modes is carried out using a temperature diagram. For example, the return of liquid with an elevated temperature will indicate high coolant costs. Underestimated data will be considered a consumption deficit.
Temperature chart 95-70:
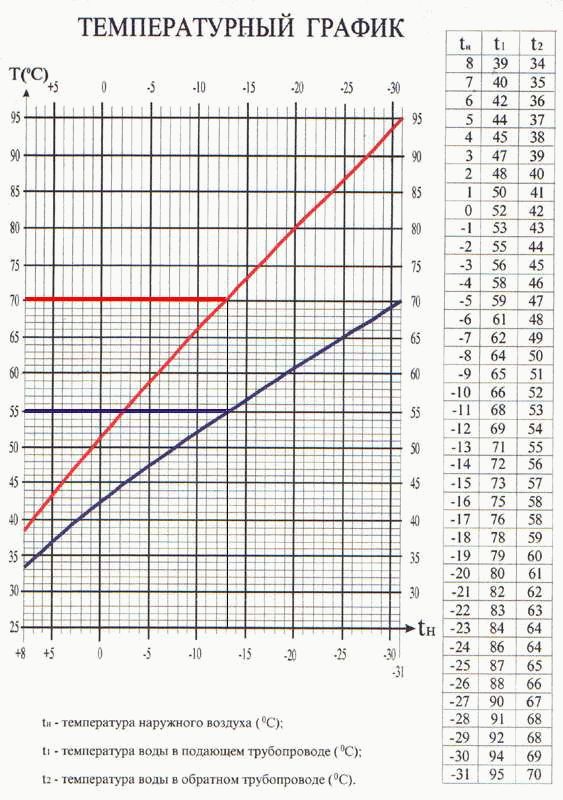
Temperature chart 95-70
A control method is selected, then a calculation is made. The calculated winter and reverse order of water supply, the amount of outside air, and the order at the break point of the diagram are taken into account. There are two diagrams: one of them considers only heating, the second considers heating with hot water consumption.
For an example of calculation, we will use the methodological development of Roskommunenergo.
The input data for the heat generating station will be:
- Tnv – the value of outside air.
- TV - indoor air.
- T1 – coolant from the source.
- T2 – reverse flow of water.
- T3 – entrance to the building.
We will look at several heat supply options with values of 150, 130 and 115 degrees.
At the same time, at the exit they will have 70°C.
The results obtained are compiled into a single table for subsequent construction of the curve:
So, we have three different schemes that can be used as a basis. It would be more correct to calculate the diagram individually for each system. Here we examined the recommended values, without taking into account the climatic features of the region and the characteristics of the building.
To reduce energy consumption, it is enough to select a low temperature setting of 70 degrees and uniform heat distribution throughout the heating circuit will be ensured. The boiler should be taken with a power reserve so that the system load does not affect the quality operation of the unit.
Automatic control is provided by the heating regulator.
It includes the following parts:
- Computing and matching panel.
- Actuating device on the water supply section.
- An actuator that performs the function of mixing liquid from the returned liquid (return).
- Boost pump and sensor on the water supply line.
- Three sensors (on the return line, on the street, inside the building). There may be several of them in the room.
The regulator closes the liquid supply, thereby increasing the value between return and supply to the value specified by the sensors.
To increase the flow, there is a boost pump and a corresponding command from the regulator. The incoming flow is controlled by a "cold bypass". That is, the temperature decreases. Some of the liquid that has circulated along the circuit is sent to the supply.
Sensors collect information and transmit it to control units, resulting in a redistribution of flows that provide a rigid temperature scheme for the heating system.
Sometimes, a computing device is used that combines hot water and heating regulators.
The hot water regulator has a simpler control scheme. The hot water sensor regulates the flow of water with a stable value of 50°C.
Advantages of the regulator:
- The temperature scheme is strictly maintained.
- Elimination of overheating of the liquid.
- and energy efficiency
- The consumer, regardless of the distance, receives heat equally.
The operating mode of boilers depends on the environmental weather.
If we take various objects, for example, a factory building, a multi-storey building and a private house, they will all have an individual thermal diagram.
In the table we show the temperature diagram of the dependence of residential buildings on outside air:
There are a number of patterns on the basis of which the temperature of the coolant in central heating changes. To track fluctuations, there are special graphs called temperature graphs. What they are and what they are needed for needs to be understood in more detail.
The temperature graph of a heating system is the dependence of the temperature of the coolant, which is water, on the temperature of the outside air.
The main indicators of the graph under consideration are two values:
- The temperature of the coolant, that is, the heated water that is supplied to the heating system to heat residential premises.
- Outdoor air temperature readings.
The lower the ambient temperature, the more it is necessary to heat the coolant that is supplied to the heating system. The schedule under consideration is constructed when designing heating systems for buildings. It determines indicators such as the size of the heating devices, the coolant flow rate in the system, as well as the diameter of the pipelines through which the coolant is transferred.
The temperature graph allows you to determine whether the coolant flow rate is too high or low. If the temperature of the returned coolant is too high, this will indicate a high flow rate. If the value is underestimated, this indicates a consumption deficit.
The reasons for temperature changes are determined by the following factors:
- When weather conditions change, heat loss automatically changes. When cold weather sets in, to ensure an optimal microclimate in apartment buildings it is necessary to expend more thermal energy than during warming. The level of heat loss consumed is calculated by the “delta” value, which is the difference between the street and indoors.
- The constancy of the heat flow from the batteries is ensured by a stable temperature of the coolant. As soon as the temperature decreases, apartment radiators will become increasingly warmer. This phenomenon is facilitated by an increase in the “delta” between the coolant and the air in the room.
The increase in coolant losses must be carried out in parallel with the decrease in air temperature outside the window. The colder it is outside, the higher the temperature of the water in the heating pipes should be. To facilitate the calculation processes, a corresponding table has been adopted.
The temperature graph for coolant supply to heating systems is a table that lists the coolant temperature values depending on the outside air temperature.
A generalized graph of water temperature in the heating system is as follows:
The formula for calculating the temperature graph is as follows:
- To determine the coolant supply temperature: T1=tin+∆xQ(0.8)+(β-0.5xUP)xQ.
- To determine the return supply temperature, the formula is used: T2=tin+∆xQ(0.8)-0.5xUPxQ.
In the presented formulas:
Q – relative heating load.
∆ is the temperature pressure of the coolant supply.
β – temperature difference in forward and reverse supply.
UP is the difference in water temperature at the inlet and outlet of the heating device.
There are two types of graphs:
- For heating networks.
- For apartment buildings.
To understand the details, let’s consider the features of the functioning of centralized heating.
The purpose of thermal power plants and heating networks is to heat the coolant to a certain value, and then transport it to the place of consumption. It is important to take into account the losses on the heating main, the length of which is usually 10 kilometers. Despite the fact that all water supply pipes are thermally insulated, it is almost impossible to avoid heat losses.
This is interesting: When will the heating be turned off: shutdown schedules and who is responsible for the shutdown 2021
When the coolant moves from a thermal power plant or simply a boiler house to the consumer (apartment building), a certain percentage of water cooling is observed. To ensure the supply of coolant to the consumer at the required standardized value, it is required to be supplied from the boiler room in the maximum heated state. However, it is impossible to increase the temperature above 100 degrees, since it is limited by the boiling point. However, it can be shifted towards increasing the temperature value by increasing the pressure in the heating system.
The pressure in the pipes according to the standard is 7-8 atmospheres, however, when the coolant is supplied, a loss of pressure also occurs. However, despite the pressure loss, a value of 7-8 atmospheres allows for efficient operation of the heating system even in 16-story buildings.
This is interesting! The pressure in the heating system of 7-8 atmospheres is not dangerous for the network itself. All structural elements remain operational in normal mode.
Taking into account the reserve of the upper temperature threshold, its value is 150 degrees. The minimum supply temperature at sub-zero temperatures outside the window is not below 9 degrees. The return temperature is usually 70 degrees.
The following restrictions apply to the home heating system:
- The maximum heating indicator is determined by a limited value of +95 degrees for a two-pipe system, as well as 105 degrees for a single-pipe network. In preschool educational institutions, stricter restrictions apply. The water temperature in the battery should not rise above 37 degrees. To compensate for the reduced temperature, additional sections of radiators are built up. Kindergartens, which are located directly in regions with harsh climatic zones, are equipped with a large number of radiators with numerous sections.
- The best option is to achieve the minimum “delta” value, which represents the difference between the supply and return values of the coolant temperature. If you do not achieve this value, then the degree of heating of the radiators will have a large difference. To reduce the difference, it is necessary to increase the speed of the coolant. However, even with an increase in the speed of movement of the coolant, a significant drawback arises, which is due to the fact that the water will return back to the thermal power plant with an excessively high temperature. This phenomenon can lead to disruptions in the functioning of the thermal power plant.
To get rid of this problem, elevator modules should be installed in every apartment building. Through such devices, a portion of supply and return water is diluted. This mixture will allow for accelerated circulation, thereby eliminating the possibility of excessive overheating of the return pipeline.
The main factor that is taken into account when calculating the temperature schedule is presented in the form of the calculated temperature in winter. When calculating heating, the outside air temperature is taken from a special table for climatic zones.
The coolant temperature table should be drawn up so that its maximum value satisfies the SNiP temperature in residential premises. For example, we use the following data:
- Radiators are used as heating devices, which supply coolant from bottom to top.
- The type of apartment heating is two-pipe, equipped with parking pipe distribution.
- The calculated values of the outside air temperature are -15 degrees.
In this case we receive the following information:
- Heating will be started when the average daily temperature does not exceed +10 degrees for 3-5 days. The coolant supply will be carried out at a value of 30 degrees, and the return will be equal to 25 degrees.
- When the temperature drops to 0 degrees, the coolant value increases to 57 degrees, and the return flow will be 46 degrees.
- At -15, water will be supplied at a temperature of 95 degrees, and the return will be 70 degrees.
This is interesting! When determining the average daily temperature, information is taken from both daytime thermometer readings and nighttime measurements.
CHP workers are responsible for the parameters of heating mains, but monitoring of networks inside residential buildings is carried out by employees of the housing office or management companies. The Housing Office often receives complaints from residents that their apartments are cold. To normalize the system parameters, you will need to take the following measures:
- Increasing the nozzle diameter or installing an elevator with an adjustable nozzle. If there is an underestimated value of the liquid temperature in the return, then this problem can be solved by increasing the diameter of the elevator nozzle. To do this, you need to close the latches and valves, and then remove the module. The nozzle is enlarged by drilling it by 0.5-1 mm. After completing the procedure, the device is returned to its place, after which the procedure of bleeding air from the system must be carried out.
- Stop the choke. To avoid the threat of the suction pump performing the function of a jumper, it is silenced. To perform this procedure, a steel pancake is used, the thickness of which should be about 1 mm. This method of temperature control belongs to the category of emergency options, since when it is carried out, it is possible that a temperature jump of up to +130 degrees may occur.
- Regulation of differences. The problem can be resolved by adjusting the differences with an elevator valve. The essence of this correction method is to redirect the hot water to the supply pipe. A pressure gauge is screwed into the return pipe, after which the valve of the return pipeline is closed. When opening the valve, you need to check the pressure gauge readings.
If you install a conventional valve, this will lead to the system stopping and freezing. To reduce the difference, you need to increase the return pressure to 0.2 atm/day. You can find out what temperature the batteries should be based on the temperature graph. Knowing its value, you can check to ensure its compliance with the temperature regime.
In conclusion, it should be noted that options for suppressing suction and regulating differences are used exclusively in the development of critical situations. Knowing this minimum of information, you can contact the housing office or thermal power plant with complaints and wishes about the coolant in the system that does not meet the standards.
The standard water temperature in the heating system depends on the air temperature. Therefore, the temperature schedule for supplying coolant to the heating system is calculated in accordance with weather conditions. In this article we will talk about the SNiP requirements for the operation of a heating system for objects for various purposes.
In order to economically and rationally use energy resources in the heating system, the heat supply is tied to the air temperature. The relationship between the temperature of the water in the pipes and the air outside the window is displayed in the form of a graph. The main task of such calculations is to maintain comfortable conditions for residents in apartments. To do this, the air temperature should be about +20…+22ºС.
The stronger the frost, the faster living spaces heated from the inside lose heat. To compensate for the increased heat loss, the temperature of the water in the heating system increases.
The standard temperature indicator is used in the calculations. It is calculated using a special method and entered into the management documentation. This indicator is based on the average temperature of the 5 coldest days of the year. For the calculation, the 8 coldest winters over a 50-year period are taken.
Why does drawing up a temperature schedule for the supply of coolant to the heating system happen this way? The main thing here is to be prepared for the most severe frosts, which happen every few years. Climatic conditions in a particular region can change over several decades. This will be taken into account when recalculating the schedule.
Useful










